Hint: Compare the characteristics of initial & final substances in order to check whether the change is physical or chemical.
Question.1. A student poured 100 mL of water in a bottle and added 40 mL vinegar to it. A balloon was filled with 20 g baking soda and was fixed at the mouth of the bottle. Slowly the shape of the balloon changed, as shown.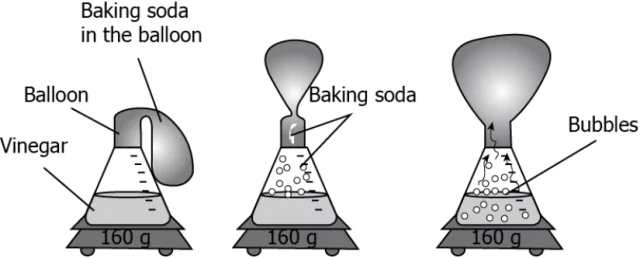
(a) Yes, as a new substance was formed in the form of a gas.
(b) Yes, as the mass remains the same throughout the experiment.
(c) No, as the formation of bubbles in the mixture shows a physical change.
(d) No, as the change in the shape and size of the balloon shows a physical change.
Question.2. A student makes a list of some activities he observes one day.
- baking a cake in an oven
- cutting an apple pie into slices
- crushing the can after drinking a soda
- carving a wooden log to make a stand
Which activity can the student classify as a chemical change?
(a) Activity 1, as the properties of the substances in the mixture change.
(b) Activity 2, as the physical state of the apple pie changes when cut.
(c) Activity 3, as the shape of the can changes.
(d) Activity 4, as the shape and size of the wooden log changes.
Ans.1. (a) Yes, as a new substance was formed in the form of a gas.
Ans.2. (a) Activity 1, as the properties of the substances in the mixture change.
Hint: Relate the substances taking part in the chemical reaction & substances formed in the chemical reaction in order to classify them as reactants & products.
Question.3. Sodium and chlorine are reacted and as a result, sodium chloride is formed which is also called table salt. What option gives the reactants and products of the reaction?
(a) reactants: sodium; products: chlorine
(b) reactants: sodium and table salt; products: chlorine
(c) reactants: tables salt; products: sodium and chlorine
(d) reactants: sodium and chlorine; products: sodium chloride
Question.4. Some chemical reactions are shown below:
H+Cl \rightarrow HCl
2H+O_{2} \rightarrow 2H_{2}O
Which option identifies the reactants and products of the reactions?
(a) Reactants: H, Cl, HCl ; Products: 2H, O_{2}, H_{2}O
(b) Reactants: HCl, 2H_{2}O ; Products: H, Cl, 2H, O_{2}
(c) Reactants: H, Cl, 2H, O_{2} ; Products: HCl, 2H_{2}O
(d) Reactants: 2H, O_{2}, H_{2}O ; Products: H, Cl, HCl
Ans.3. (d) reactants: sodium and chlorine; products: sodium chloride
Ans.4. (c) Reactants: H, Cl, 2H, O_{2} ; Products: HCl, 2H_{2}O
Hint: Use chemical symbols & chemical formulae correctly in order to acquire the skill of writing chemical equations.
Question.5. A student performs an experiment to form aluminium chloride from aluminium and chlorine. Which options gives the chemical equation of the reaction?
(a) Al+Cl_{2} \rightarrow AlCl_{2}
(b) 2Al+Cl_{2} \rightarrow 2AlCl
(c) 2Al+3Cl_{2} \rightarrow 2AlCl_{3}
(d) 2Al+3Cl_{2} \rightarrow 3AlCl_{3}
Question.6. A researcher adds barium hydroxide to hydrochloric acid to form a white-colored barium chloride. Which option gives the balanced chemical equation of the reaction?
(a) HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaCl_{2}+2HOH
(b) 2HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaCl_{2}+2HOH
(c) 2HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaH_{2}+2HCl+O_{2}
(d) HCl+2Ba(OH) \rightarrow 2BaCl_{2}+2HOH+O_{2}
Ans.5. (c) 2Al+3Cl_{2} \rightarrow 2AlCl_{3}
Ans.6. (b) 2HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaCl_{2}+2HOH
Hint: Apply Law of Conservation of Mass in order to balance chemical equations.
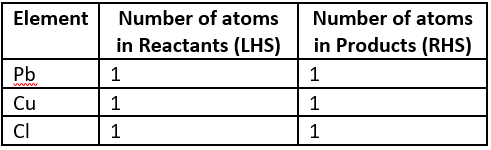
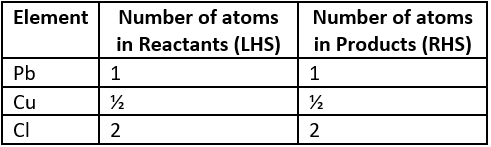
Question.7. A student writes a balanced chemical equation.
Pb(s)+CuCl_{2} (aq) \rightarrow PbCl_{2}+Cu(s)
Which option gives the number of elements on the LHS and RHS of the chemical equation?
(a) 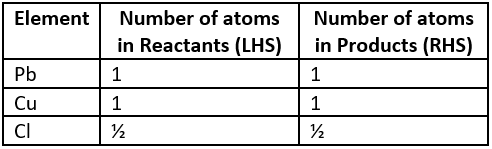
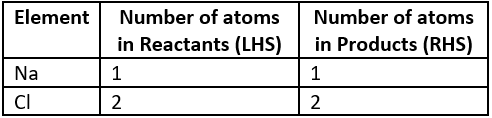
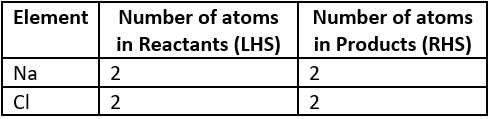
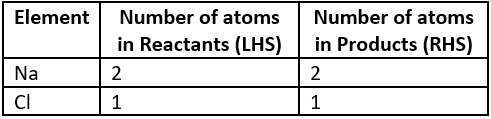
Question.8. A balanced chemical equation of the reaction between sodium and chlorine to form sodium chloride is shown below:
2Na+Cl_{2} \rightarrow NaCl
Which option shows the number of atoms on both sides of the reaction?
(a) 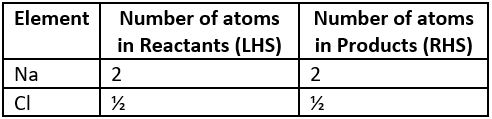
Ans.7. (d) 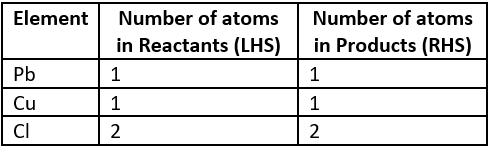
Hint: Categorize the given reactions as (combination / decomposition) based on the reactants & products of a chemical reaction.
Question.9. A student writes a chemical equation of the reaction between carbon monoxide and hydrogen.
CO_{2}+2H_{2} \rightarrow CH_{3}OH
How can the reaction be classified?
(a) The reaction is an example of a combination reaction as a compound separates into two compounds.
(b) The reaction is an example of a decomposition reaction as a compound dissociates into two compounds.
(c) The reaction is an example of a combination reaction as two compounds react to form a single compound.
(d) The reaction is an example of a decomposition reaction as two compounds react to form a single compound.
Question.10. A student learns that some products are formed as a result of combining two compounds while some compounds are formed as a result of dissociation of two compounds. The two reactions are
P: CaO+SO_{2} \rightarrow CaSO_{3}
Q: ZnCO_{3} \rightarrow ZnO+CO_{2}
Which reaction is an example of a combination reaction and a decomposition reaction?
(a) both the reactions are examples of combination reaction
(b) both the reactions are examples of a decomposition reaction
(c) reaction P is an example of a combination reaction while reaction Q is an example of a decomposition reaction
(d) P is an example of a decomposition reaction while reaction Q is an example of a combination reaction
Ans.9. (c) The reaction is an example of a combination reaction as two compounds react to form a single compound.
Ans.10. (c) reaction P is an example of a combination reaction while reaction Q is an example of a decomposition reaction
Hint: Classify the given reaction as displacement or double displacement based on the type of reactants used & products formed.
Question.11. A student adds lead and silver to two different test tubes containing an equal amount of copper sulphate solution. The student observes that the color of the solution in the test tube with lead changes. What explains the change in the colour of the solution?
(a) A displacement reaction takes place as lead replaces copper from the solution.
(b) A combination reaction takes place as lead combines with sulphate in the solution.
(c) decomposition reaction takes place as copper dissociates from sulphate in the solution.
(d) A double displacement reaction takes place as copper dissociates from sulphate and lead combines with sulphate in the solution.
Question.12. The chemical reaction between potassium chloride and silver nitrate is given by the chemical equation.
AgNO_{3}+KCl \rightarrow AgCl+KNO_{3}
What can be inferred from the chemical equation?
(a) silver nitrate and potassium undergo a decomposition reaction to form silver chloride and potassium nitrate
(b) silver nitrate and potassium undergo a displacement reaction to form silver chloride and potassium nitrate
(c) silver nitrate and potassium undergo a combination reaction to form silver chloride and potassium nitrate
(d) silver nitrate and potassium undergo double displacement reaction to form silver chloride and potassium nitrate
Ans.11. (a) A displacement reaction takes place as lead replaces copper from the solution.
Ans.12. (d) silver nitrate and potassium undergo double displacement reaction to form silver chloride and potassium nitrate.
Hint: Predict the reaction as Oxidation or Reduction based on the addition/ removal of oxygen/ hydrogen/ electrons to the reactants to form products.
Question.13. The reaction between zinc and hydrogen is shown below:
Zn+2H^{+} \rightarrow Zn^{2+}+H_{2}
Which option shows oxidation?
(a) Zn \rightarrow Zn^{2+}
(b) 2H^{+} \rightarrow H_{2}
(c) Zn^{+2} \rightarrow Zn
(d) H_{2} \rightarrow 2H^{+}
Question.14. The reaction between iron oxide and hydrogen is shown below:
Fe_{3}O_{4}+4H_{2} \rightarrow 3Fe+4H_{2}O
Which option shows the compounds undergoing oxidation and reduction?
(a) Oxidation: 4H_{2} Reduction: 3Fe
(b) Oxidation: 3Fe Reduction: 4H_{2}
(c) Oxidation: Fe_{3}O_{4} Reduction: 4H_{2}O
(d) Oxidation: 4H_{2}O Reduction: Fe_{3}O_{4}
Ans.13. (a) Zn \rightarrow Zn^{2+}
Ans.14. (a) Oxidation: 4H_{2} Reduction: 3Fe
Hint: Observe colour change in iron, copper and silver articles over time in order to outline the effects of corrosion in our surroundings (real life situations, stating any two).
Question.15. A student notices that a new hammer made of iron is shiny while an old one kept in the toolbox for long has a reddish-brown powder deposit over it. What does the change in colour of the hammer indicate?
(a) effect of moisture on metals
(b) iron hammer turns brown after some time
(c) effects of kept in a box for a longer duration
(d) iron changes colour when kept with other tools
Question.16. A student notices that her silver jewellery turned dull and had a gray-black film over it after wearing for a few months. What results in the change in colour of the silver metal?
(a) dust deposits over the jewellery which changes its colour
(b) the jewellery comes in contact with air, moisture, and acids and corrodes
(c) the polish over the jewellery was removed after wearing for a few months
(d) silver breaks due to wear and tear and turns its colour changes due to rusting
Ans.15. (a) effect of moisture on metals
Ans.16. (b) the jewellery comes in contact with air, moisture, and acids and corrodes
Hint: Detect changes in smell, colour, taste of food items overtime, in order to explain effects of oxidation on food items.
Question.17. A student learns that food companies fill bags of chips with nitrogen gas. What is the purpose packing it with nitrogen?
(a) it prevents rancidity of chips
(b) it keeps the mosquitoes away from chips
(c) it keeps the chips dry if the pack falls in water
(d) prevents chips from spilling out when the pack is opened
Question.18. A student notices that the bread kept out has a green coloured coating over it after a few days. What explains the reason for the student’s observation?
(a) the oils in the bread oxidises and causes rancidity
(b) bread comes in contact with atmospheric moisture and corrodes
(c) the oils in the bread reduces and cause the change in the colour of the bread
(d) comes in contact with the atmospheric nitrogen and a layer deposit over it
Ans.17. (a) it prevents rancidity of chips
Ans.18. (a) the oils in the bread oxidises and causes rancidity