What is Case Study Question / Paragraph Based Question?
A case study is a scenario in a particular academic / professional context which students are expected to analyse and respond to, guided by specific questions posed concerning the situation. In many cases, the scenario or case study involves a number of issues or problems that must be dealt with in a academic / professional workplace.
Why Case Study Questions are included in academics?
Case study assignments usually require students to identify problems and issues in a scenario, to demonstrate their developing knowledge of theories and academic / professional policies and to make decisions and recommendations based on these to either prevent or solve some of the issues in that scenario.
How to solve Case Study Questions?
There are several steps to writing an answer to a case study assignment:
STEP 1: Read the case study and questions carefully.
- Read the case and associated questions carefully.
- Highlight the main points of the case and any issues that you can identify.
- Read the questions closely and analyse what they are requiring you to do.
- Read the case again, linking the information that is relevant to each question you have been asked.
STEP 2: Identify the issues in the case study.
Case studies describe a situation which may arise in a particular profession or social context. They often involve a number of people in a complex situation. They will often describe a situation which is problematic, possibly in how it is dealt with, or in its complexity. An important part of your answer is to analyse the situation and to identify the issues/actions described in the case which may be problematic. The following questions may help you to do this:
- What actions were taken in the case?
- Were these actions the most appropriate and why?
- Were there any consequences of the actions taken?
- Was anything omitted or not considered?
- Were actions/procedures in line with existing codes of practice, policy or theories?
STEP 3: Link theory to practice.
Use your knowledge of existing codes of practice, theories and/or other academic / professional documents and behaviours to decide what was done appropriately and what was not.
STEP 4: Plan your answer.
It can be useful to use the questions you have been set as headings and to answer each part in turn, reducing the chance of omitting set questions. You can always take out the headings before you submit if you wish. Lecturers usually set questions in a logical order, so answer in the order they are written in your question.
STEP 5: Start writing your case study answer (for theory only)
Like any assignment, you will need an introduction, body sections in which you answer the questions put to you regarding the case study, and a conclusion.
STEP 6: Edit and proofread.
Read through your paper yourself to detect and correct other errors and omissions.
Check you have answered all questions and backed up your answer with relevant passage.
Types of Case Study Questions / Paragraph Based Questions
Case Study Questions / Paragraph Based Questions can be broadly classified into two types:
- MCQs type: In this type, student has to tick the correct option from various options.
- Theory type: In this type, student has to write proper solution / answer in cotext to the case study.
Case Study/ Passage Based Questions Chapter 1 Resources and Development
Type 1: MCQ type
Case Study Question 01
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
We live on land, we perform our economic activities on land and we use it in different ways. Thus, land is a natural resource of utmost importance. It supports natural vegetation, wild life, human life, economic activities, and transport and communication systems. However, land is an asset of a finite magnitude, therefore, it is important to use the available land for various purposes with careful planning. India has land under a variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains and islands. About 43 per cent of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. Mountains account for 30 per cent of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. About 27 per cent of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question.1. The land should be used in a optimum way, because land is a _________ resource. Choose the correct option:
(a) Finite
(b) Infinite
(c) Abiotic Resource
(d) None of these
(a) Finite.
Question.2. Land Resource planning means careful use of available land. Identify which landform the following commercial activities belong to: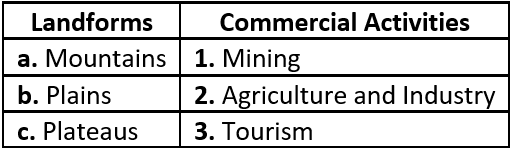
(a) a-2, b-1, c-3
(b) a-3, b-2, c-1
(c) a-1, b-3, c-2
(d) a-3, b-1, c-2
(b) a-3, b-2, c-1
Question.3. Which one of the following options does not suit with land utilisation?
(a) Constructing roads and infrastructure on hills to promote tourism.
(b) Developing canal systems in the plains to boost agriculture.
(c) Providing government support to establish mineral based industry near the mining areas.
(d) Boosting the industries on fertile land near the densely populated areas.
(d) Boosting the industries on fertile land near the densely populated areas.
Question.4. In order to make the best use of Himalayan region. India should not:
(a) Allow large scale deforestation to construct industries.
(b) Help local artisans and handicrafts to boost tourism.
(c) Preserve natural flora and fauna.
(d) Conserve the flow of rivers.
(a) Allow large scale deforestation to construct industries.
Case Study Question 02
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question.1. In which of the following states deforestation due to mining has caused several land degradations?
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Odisha
(c) Chhattisgarh
(d) All of these
(d) All of these
Question.2. Which is the main reason for land degradation Rajasthan?
(a) Deforestation
(b) Over-grazing
(c) Over irrigation
(d) Mineral processing
(b) Over-grazing
Question.3. Which is the main reason for land degradation in Jharkhand?
(a) Deforestation
(b) Over-grazing
(c) Over irrigation
(d) Mineral processing
(a) Deforestation
Question.4. In which of the following states over-grazing is the main reason for land degradation?
(a) Gujarat
(b) Chhattisgarh
(c) Punjab
(d) Haryana
(c) Punjab
Case Study Question 03
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
India has land under a variety of relief features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains and islands. About 43 per cent of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. Mountains account for 30 percent of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. About 27 per cent of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question.1. What percent of the land area is plain?
(a) 27
(b) 30
(c) 33
(d) 43
(d) 43
Question.2. What percentage of land area is mountain?
(a) 27
(b) 30
(c) 33
(d) 43
(b) 30
Question.3. Which relief features of India perennial flow of some rivers?
(a) Plains
(b) Plateaus
(c) Mountains
(d) Forests
(c) Mountains
Question.4. Which relief features processes rich Reserve of minerals, fossils fuels and forests?
(a) plains
(b) mountains
(c) plateau
(d) oceans
(c) plateau
Case Study Question 04
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
In June 1992, more than 100 heads of states met in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil, for the first International Earth Summit. The Summit was convened for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socioeconomic development at the global level. The assembled leaders signed the Declaration on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity. The Rio Convention endorsed the global Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question.1. Where was the first international Earth Summit held?
(a) New York
(b) Brazil
(c) London
(d) Mexico
(b) Brazil
Question.2. When was the first international Earth summit held?
(a) January 1992
(b) March 1992
(c) June 1992
(d) July 1992
(c) June 1992
Question.3. How many heads of states met for the first international Earth summit?
(a) 92
(b) 100
(c) 21
(d) 19
(b) 100
Question.4. Which declaration was signed by the assembled leaders?
(a) Global Climatic Change
(b) Biological diversity
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Case Study Question 05
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
Read the article from a Kenyan newspaper:
“In August 2015—after a couple of years of testing — a company in Kenya began commercially treating human poop with the sun’s heat to create an environmentally friendly fuel source.
This week, Sanivation plans to turn on a new continuous-flow system that will help it scale up to support many more customers than it could previously.
“We can treat thousands and multi-thousands of peoples’ shit continuously,” says Sanivation CTO Emily Woods.
In developing countries, the International Energy Agency estimates that about 2.5 billion people cook with biomass: charcoal from forests, agricultural waste, animal dung, and other sources. In Kenya, charcoal provides about 82 percent of the energy in urban households and 34 percent of the energy in rural households, according to the Kenya Forest Service.
Yet its use is leading to major deforestation—2013 research found that the demand for charcoal was about 16.3 million m3, but there was only a supply of about 7.3 million m3. Not to mention that the air pollution from inefficiently burning solid fuels such as charcoal can kill about 4.3 million people a year.
One solution to these problems could be switching to cleaner cooking stoves, but some research points out that new technology adoption is difficult. Instead of swapping stoves, changing fuel is another possibility— research by the United Nations University Institute for Water, Environment, and Health concluded that the electricity generated from the world’s collective human feces could power up to 138 million households, for example. And that’s where Sanivation steps in—providing an alternative cooking-fuel source to local small businesses and restaurants. Woods says Sanivation’s sun-treated poop fuel briquettes can burn two times longer than normal charcoal, yet release about one third of the carbon monoxide and particulate matter emissions. Each metric ton of the briquettes saves about 88 trees yet they are “comparable” in cost even with charcoal’s rapid price fluctuations.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
Question.1. Which of the following is not a fuel of rural mass in most developing or underdeveloped nations?
(a) LPG
(b) Charcoal
(c) Agricultural waste
(d) Animal dung
(a) LPG
Question.2. The air pollution from inefficiently burning solid fuels such as charcoal can kill about 4.3 million people a year. Which of the following sentence is directly linked with the killing of people by air pollution?
(a) Insufficient burning of solid fuels emits poisonous gases like carbon monoxide.
(b) The air pollution caused might lead to serious disease in human beings in long run.
(c) Use of charcoal lead to deforestation & global warming.
(d) All of the above.
(d) All of the above
Question.3. How sun-treated poop fuel briquettes are a greener option than wood charcoal?
Sun-treated poop fuel briquettes can burn two times longer than normal charcoal, yet release about one third of the carbon monoxide and particulate matter emissions.
- Each metric ton of the briquettes saves about 88 trees yet they are “comparable” in cost even with charcoal’s rapid price fluctuations.
So these are more useful than charcoal.
Case Study Question 06
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion. The processes of soil formation and erosion, go on simultaneously and generally there is a balance between the two. Sometimes, this balance is disturbed due to human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, construction and mining etc., while natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion. The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land. In the Chambal basin such lands are called ravines.
Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion. Wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land known as wind erosion. Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming. Ploughing in a wrong way i.e. up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion.
Answer the following questions:
Question.1. In which of the following cases wind erosion will be minimum
(a) Surface with loose soil
(b) Grass covered land
(c) Sandy soil
(d) Sloping land
(b) Grass covered land
Question.2.State whether the following statement is true or false.
- The process of soil formation can happen without soil erosion.
False
Question.3. Write one major difference between the structure of the lands affected by Gully erosion and sheet erosion.
The lands affected by Gully erosion have deep and steep depths as compared to land with sheet erosion where only top soil is removed and more silt and pebbles are visible.
Also it is difficult to make the gully eroded area covering with vegetation as compared to sheet erosion land.
Case Study Question 07
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
Resources are vital for any developmental activity. But irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to socioeconomic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various levels is important. This had been the main concern of the leaders and thinkers in the past. For example, Gandhiji was very apt in voicing his concern about resource conservation in these words: “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed.” He placed the greedy and selfish individuals and exploitative nature of modern technology as the root cause for resource depletion at the global level. He was against mass production and wanted to replace it with the production by the masses.
Question.1. Resources are vital for
(a) Developmental activity
(b) Commercial activity
(c) Social activity
(d) Environmental activity
(a) Developmental activity
Question.2.Irrational consumption and over-utilisation of resources may lead to ____________.
Socioeconomic and environmental problems
Question.3. “There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed.” Who said this?
Mahatma Gandhiji
Type 2: Theory Type
Case Study Question 01
Read the source given below and answer the question that follows:
Source A-Alluvial soils
Alluvial soils as a whole are very fertile. Mostly these soils contain adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops. Due to its high fertility, regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated. Soils in the drier areas are more alkaline and can be productive after proper treatment and irrigation.
Source B- Black Soil
Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil. It is believed that climatic condition along with the parent rock material are the important factors for the formation of black soil. This type of soil is typical of the Deccan trap (Basalt) region spread over northwest Deccan plateau and is made up of lava flows. They cover the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh and extend in the south east direction along the Godavari and the Krishna valleys.
Source A-Alluvial soils
Question.1. How alkaline soil can be made productive?
The alkaline soil can be made productive after proper treatment and irrigation.
Source B-Black Soil
Question.2. How does the black soil formed?
Ans.2. The Black soil is made up of lava flows.
Case Study Question 02
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion. The processes of soil formation and erosion, go on simultaneously and generally there is a balance between the two. Sometimes, this balance is disturbed due to human activities like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc., while natural forces like wind, glacier and water lead to soil erosion. The running water cuts through the clayey soils and makes deep channels as gullies. The land becomes unfit for cultivation and is known as bad land. In the Chambal basin such lands are called ravines. Sometimes water flows as a sheet over large areas down a slope. In such cases the top soil is washed away. This is known as sheet erosion. Wind blows loose soil off flat or sloping land known as wind erosion. Soil erosion is also caused due to defective methods of farming. Ploughing in a wrong way i.e. up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion. Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called contour ploughing. Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts erosion. Western and central Himalayas have well developed terrace farming. Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind. This method is known as strip cropping. Planting lines of trees to create shelter also works in a similar way. Rows of such trees are called shelter belts. These shelter belts have contributed significantly to the stabilisation of sand dunes and in stabilising the desert in western India.
Question.1. Which land is known as bad land? In what basin such lands is known as ravines?
The land that becomes unfit for cultivation is known as bad land. In Chambal basin such lands is known as ravines.
Question.2. What do you understand by sheet erosion?
When top soil is washed away by the flows of water then this type of erosion is called sheet erosion.
Question.3. How does ploughing leads to the erosion? For what reasons balance between soil erosion and soil formation is disturbed?
Ploughing in a wrong way i.e. up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion. Activities of humans like deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc. cause disturbance between soil formation and erosion.
Case Study Question 03
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
Question.1. Aman lives in a village in Punjab. What may be the reason of land degradation around his village?
Salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
Question.2. In which state over grazing is one of the reason for land degradation?
In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
Question.3. State any two reasons of land degradation done by human activities.
- Mining in the regions of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha.
- Over irrigation in Punjab, Haryana & western UP.
Case Study Question 04
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
The history of colonisation reveals that rich resources in colonies were the main attractions for the foreign invaders. It was primarily the higher level of technological development of the colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the colonies. Therefore, resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes. India has experienced all this in different phases of colonisation. Therefore, in India, development, in general, and resource development in particular does not only involve the availability of resources, but also the technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people.
Question.1. What helped the colonising countries establish their supremacy over the colonies?
The higher level of technological development of the colonising countries.
Question.2. What were the main attraction for the foreign invaders?
Rich resources in colonies were the main attractions for the foreign invaders.
Question.3. What were the factor involved for development in India?
The technology, quality of human resources and the historical experiences of the people were the factor involved for development in India.
Case Study Question 05
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Arid soils range from red to brown in colour. They are generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water. Due to the dry climate, high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture. The lower horizons of the soil are occupied by Kankar because of the increasing calcium content downwards. The Kankar layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water. After proper irrigation these soils become cultivable as has been in the case of western Rajasthan.
Question.1. In which state of India Arid Soil is found in abundance?
Rajasthan
Question.2. In arid soil the infiltration of water is restricted. Why?
The Kankar layer formations in the bottom horizons restrict the infiltration of water in Arid Soil.
Question.3. How can the Arid Soil be made cultivable?
After proper irrigation Arid soils become cultivable. In the Rajasthan region after proper irrigation facilities the cultivable lands are increasing.
Case Study Question 06
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
FOSSIL FUELS
Fossil fuels are fuels produced from the remains of ancient plants and animals. They include coal, petroleum (oil), and natural gas. People rely on fossil fuels to power vehicles like cars and airplanes, to produce electricity, and to cook and provide heat.
In addition, many of the products we use today are made from petroleum. These include plastics, synthetic rubber, fabrics like nylon, medicines, cosmetics, waxes, cleaning products, medical devices, and even bubble-gum.
Fossil fuels formed over millions of years. Once we use them up, we cannot replace them. Fossil fuels are a non-renewable resource.
We need to conserve fossil fuels so we don’t run out. However, there are other good reasons to limit our fossil fuel use. These fuels pollute the air when they are burned. Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Global warming is changing ecosystems. The oceans are becoming warmer and more acidic, which threatens sea life. Sea levels are rising, posing risks to coastal communities. Many areas are experiencing more droughts, while others suffer from flooding.
Scientists are exploring alternatives to fossil fuels. They are trying to produce renewable biofuels to power cars and trucks. They are looking to produce electricity using the sun, wind, water, and geothermal energy— Earth’s natural heat.
Everyone can help conserve fossil fuels by using them carefully. Turn off lights and other electronics when you are not using them. Purchase energy-efficient appliances and weatherproof your home. Walk, ride a bicycle, carpool, and use public transportation whenever possible.
Question.1. Why fossil fuels are contributing to global warming?
Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
Question.2. Enlist 4 alternatives to produce electricity besides fossil fuel.
Four alternatives to produce electricity besides fossil fuel are using the sun, wind, water, and geothermal energy which are renewable sources of energy.
Question.3. Even you use Carpool system to travel office, one car also contributes to pollution. Explain how it reduces pollution by minimum 4 times?
Car-pooling can reduce pollution by minimum 4 times as a single car can accommodate 4 or more passengers and work efficiently by saving fuel of other 3 car users who might have travelled alone if there were no car-pooling.
Case Study Question 07
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
We have shared our land with the past generations and will have to do so with the future generations too. Ninety-five per cent of our basic needs for food, shelter and clothing are obtained from land. Human activities have not only brought about degradation of land but have also aggravated the pace of natural forces to cause damage to land. Some human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, mining and quarrying too have contributed significantly in land degradation. Mining sites are abandoned after excavation work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of overburdening. In states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation due to mining have caused severe land degradation. In states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation. In the states of Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh, over irrigation is responsible for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil. The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere. It retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land. In recent years, industrial effluents as waste have become a major source of land and water pollution in many parts of the country.
Answer the following questions:
Question.1. With whom do we share our land?
With the past generations and will have to do so with the future generations too.
Question.2. Name some Indian states which are deforested due to mining and overgrazing activities.
Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh
Question.3. What harm does the mineral processing and cement industry do to the environment and land?
Generate huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere
Case Study Question 08
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Resources are vital for human survival as well as for maintaining the quality of life. It was believed that resources are free gifts of nature. As a result, human beings used them indiscriminately and this has led to the following major problems.
- Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of a few individuals.
- Accumulation of resources in few hands, which, in turn, divided the society into two segments i.e. haves and have nots or rich and poor.
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation. An equitable distribution of resources has become essential for a sustained quality of life and global peace. If the present trend of resource depletion by a few individuals and countries continues, the future of our planet is in danger. Therefore, resource planning is essential for the sustainable existence of all forms of life.
Sustainable existence is a component of sustainable development.
Fill in the blanks:
Question.1. Resources are vital for human survival as well as for maintaining the quality of __________.
Life
Question.2. _______ existence is a component of sustainable development.
Sustainable
Question.3. Resource __________ is essential for sustainable existence of all forms of life.
Planning
Case Study Question 09
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
In June 1992, more than 100 heads of states met in Rio De Janeiro in Brazil, for the first International Earth Summit. The Summit was conveyed for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socioeconomic development at the global level. The assembled leaders signed the Declaration on Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity. The Rio Convention endorsed the global Forest Principles and adopted Agenda 21 for achieving Sustainable Development in the 21st century.
Question.1. Which declaration was signed by the assembled leaders?
Global Climatic Change and Biological Diversity
Question.2. Agenda 21 was adopted for achieving ____________ in the 21st century.
Sustainable Development
Question.3. What does the first international Earth Summit conveyed?
The first international Earth Summit was conveyed for addressing urgent problems of environmental protection and socioeconomic development at the global level.
Case Study Question 10
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
India has land under a variety of relief features, namely mountains, plateaus, plains and island. About 43% of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry. Mountains account for 30% of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects. About 27% of the area of the country is the plateau region. It possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
Question.1. 43% of the land provides facilities for ____________.
Agriculture and industry
Question.2. What features does mountain of India possess?
Mountains account for 30% of the total surface area of the country and ensure perennial flow of some rivers, provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects.
Question.3. What proportion of land area is covered with plateau?
About 27% of the area of the country is the plateau region.
Case Study Question 11
Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Soil erosion is also caused due to the defective methods of farming. Ploughing in a wrong way i.e., up and down the slope form channels for the quick flow of water leading to soil erosion. Ploughing along the contour line can be decelerate the flow of water down the slopes. This is called Contour Ploughing. Steps can be cut out on the slopes making terrace. Terrace cultivation restrict erosion. Western and Central Himalayas have were developed terrace farming.
Question.1. When water descends the slope which lines slow the water’s flow?
Contour
Question.2. Mention the region with well-developed terrace farming.
Western and central Himalayas
Question.3. What impact did ploughing have on the farming method leads to soil erosion?
Ploughing disturbs the natural soil surface and protective vegetation which leads to increase in erosion and which moves fertile farm soil into bodies of water.


