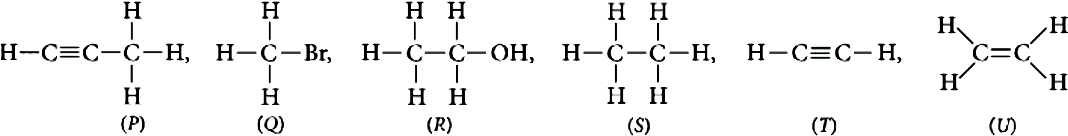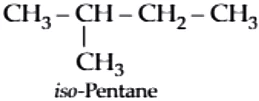Case Study Question 01
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
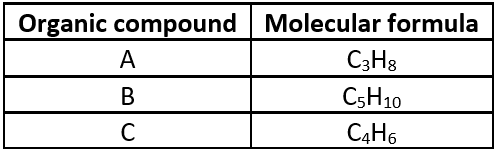
Study the table related to three hydrocarbons A, B, C and answer the questions that follow.
Question.1. A, B and C are classified as hydrocarbons because
(a) they contain hydrogen
(b) they contain carbon
(c) they contain both carbon and hydrogen
(d) none of these
Question.2. Which of these organic compounds is an alkyne?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) All of these
Question.3. C_{5}H_{10} belongs to
(a) C_{n}H_{2n+2} series
(b) C_{n}H_{2n} series
(c) C_{n}H_{2n-2} series
(d) none of these.
Question.4. Identify the incorrect statement about these three hydrocarbons.
(a) All have different general formula
(b) A and B differ by -CH_{2} unit
(c) C is an alkyne
(d) B is an alkene.
Question.5. General formula for alkane is
(a) C_{n}H_{2n}
(b) C_{n}H_{2n+2}
(c) C_{n}H_{2n-2}
(d) C_{n}H_{n}
Ans.1. (c)
A, B and C are classified as hydrocarbons because these compounds are made up of carbon and hydrogen only.
Ans.2. (c)
C is an alkyne.
Ans.3. (b)
C_{5}H_{10} is an alkene having a general formula C_{n}H_{2n} .
Ans.4. (b)
A and B do not belong to same homologous series. A is an alkane while B is an alkene.
Ans.5. (b)
Case Study Question 02
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
Question.1. Which of the following compounds belong to same homologous series?
(a) S and T
(b) T and U
(c) P and U
(d) P and T
Question.2. The functional group of compound (R) is
(a) alcohol
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) carboxylic acid.
Question.3. Compound (T) belongs to homologous series of
(a) alkynes
(b) alkenes
(c) alkanes
(d) none of these.
Question.4. Which of the following compounds is unsaturated hydrocarbon?
(a) S
(b) Q
(c) U
(d) R
Question.5. Which of the following compounds belongs to alkane series?
(a) P
(b) S
(c) T
(d) U
Ans.1. (d)
(P) and (T) are alkynes.
Ans.2. (a)
Alcohol (-OH).
Ans.3. (a)
(T) is an alkyne having general formula of homologous series C_{n}H_{2n-2} .
Ans.4. (c)
(U) is an alkene.
Ans.5. (b)
Case Study Question 03
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
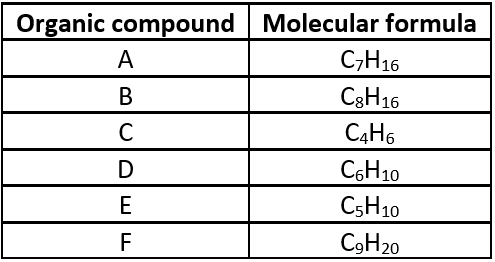
The table given below shows six organic compounds A, B, C, D, E and F having different molecular formula:
Question.1. Which of the following compounds belong to same homologous series?
(a) E and F
(b) B and C
(c) A and B
(d) C and D
Question.2. Which of the following is the member of the same homologous series as E?
(a) D
(b) A
(c) F
(d) B
Question.3. Identify the correct statements.
(a) A and F are saturated hydrocarbons while all others are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(b) C and D belong to a homologous series having general formula C„H2
(c) B and E are alkynes.
(d) All the compounds have same physical and chemical properties.
Question.4. Compound B is
(a) an alkane
(b) an alkene
(c) an alkyne
(d) none of these
Question.5. Compound (F) has a general formula
(a) C_{n}H_{2n-2}
(b) C_{n}H_{2n}
(c) C_{n}H_{2n+4}
(d) C_{n}H_{2n+2}
Ans.1. (d)
A and F are alkanes ; B and E are alkenes ; C and D are alkynes.
Ans.2. (d)
B is an alkene having general formula C_{n}H_{2n} , the homologous series to which E belongs.
Ans.3. (a)
C and D belong to a homologous series having general formula C_{n}H_{2n-2} . B and E are alkenes. All the compounds have different physical and chemical properties.
Ans.4. (b)
(B) is alkene.
Ans.5. (d)
(F) is an alkane.
Case Study Question 04
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
A hydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C_{10}H_{22} . A hydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. A hydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belong to the same homologous series.
Question.1. What is the molecular formula of (Q)?
(a) C_{12}H_{26}
(b) C_{8}H_{16}
(c) C_{8}H_{18}
(d) C_{8}H_{14}
Question.2. To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
(a) C_{n}H_{2n}
(b) C_{n}H_{2n-2}
(c) C_{n}H_{2n+2}
(d) C_{n}H_{2n+1}
Question.3. What is the molecular formula of (R)?
(a) C_{12}H_{26}
(b) C_{12}H_{24}
(c) C_{12}H_{22}
(d) C_{12}H_{28}
Question.4. Identify the correct statement about compounds (P), (Q) and (R).
(a) They have same melting and boiling points.
(b) They have same chemical properties.
(c) They have different general formula.
(d) They differ by -CH_{2} unit.
Question.5. Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are
(a) alkanes
(b) alkenes
(c) alkynes
(d) none of these.
Ans.1. (c)
Molecular formula of (Q) is C_{8}H_{18} as it has two carbon atoms less than (P).
Ans.2. (c)
Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are alkanes having general formula C_{n}H_{2n+2}
Ans.3. (a)
Molecular formula of (R) is C_{12}H_{26} as it has two carbon atoms more than (P).
Ans.4. (b)
Compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong to same homologous series so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties. They have same general formula C_{n}H_{2n+2} . They differ by 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms.
Ans.5. (a)
Case Study Question 05
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
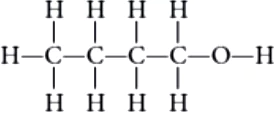
An organic molecule has the following structure:
Question.1. To which homologous series does this molecule belong?
(a) Aldehydes
(b) Ketones
(c) Alcohols
(d) Alkanes
Question.2. What is the general formula of this homologous series?
(a) C_{n}H_{2n+1}OH
(b) C_{n}H_{2n+2}
(c) C_{n}H_{2n}O
(d) C_{n}H_{2n+1}CHO
Question.3. Which is the next member of this series?
(a) C_{4}H_{9}OH
(b) C_{3}H_{7}OH
(c) C_{5}H_{11}OH
(d) C_{6}H_{13}OH
Question.4. Which is the third member of this series?
(a) C_{3}H_{7}OH
(b) C_{4}H_{9}OH
(c) C_{2}H_{5}OH
(d) CH_{3}OH
Question.5. Which is the second member of this series?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Methanol
(c) Propanol
(d) Butanol
Ans.1. (c)
Alcohol (-OH).
Ans.2. (a)
C_{n}H_{2n+1}OH is the general formula of the homologous series of alcohol.
Ans.3. (c)
Ans.4. (a)
Ans.5. (a)
Ethanol; C_{2}H_{5}OH is the second member of this series.
Case Study Question 06
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
A series of organic compounds having same functional group, with similar or almost identical chemical characteristics in which all the members can be represented by the same general formula and the two consecutive members of the series differ by -CH_{2} group or 14 mass unit in their molecular formulae is called a homologous series. For example, all the members of alcohol family can be represented by the general formula, C_{n}H_{2n+1}OH where, n may have the values 1, 2, 3, … etc. The various members of a particular homologous series are called homologues. The physical properties such as density, melting point, boiling point, solubility, etc. of the members of a homologous series show almost regular variation in ascending or descending the series.
Question.1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of members of a homologous series?
(a) They possess varying chemical properties.
(b) Their physical properties vary in regular and predictable manner.
(c) Their formulae fit the general molecular formula.
(d) Adjacent members differ by one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.
Question.2. All the members of homologous series of alkynes have the general formula
(a) C_{n}H_{2n}OH
(b) C_{n}H_{2n+2}OH
(c) C_{n}H_{2n-2}OH
(d) C_{n}H_{2n-4}OH
Question.3. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) A common functional group is present in different members of a homologous series.
(b) Two consecutive members of a homologous series differ by a -CH_{3} group.
(c) The molecular mass of a compound in the series differs by 14 a.m.u. from that of its neighbour.
(d) All the members of a homologous series have common general methods of preparation.
Question.4. Identify the correct statements.
(I) As the molecular mass increases in any homologous series, a gradation in physical properties is seen.
(II) The melting and boiling points decrease with increasing molecular mass.
(III) Other physical properties such as solubility in a particular solvent decreases with increasing molecular mass.
(IV) The chemical properties, which are determined solely by the functional group, remain similar in a homologous series.
(a) (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (III) and (IV)
(b) (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II), (III) and (IV)
Question.5. The table shows the formulae of three organic compounds that belong to the same homologous series.
- First member of the homologous series CH_{3}-O-CH_{3}
- Second member of the homologous series CH_{3}CH_{2}-O-CH_{3}
- Third member of the homologous series CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}-O-CH_{3}
What is the general formula of this series?
(a) C_{n}H_{2n}O
(b) C_{n}H_{2n+2}O
(c) C_{n}H_{2n}OH
(d) C_{n}H_{2n+2}OH
Ans.1. (a)
All the members of homologous series show similar chemical properties.
Ans.2. (c)
Alkynes have the general formula C_{n}H_{2n-2} e.g., Ethyne ( C_{2}H_{2} ), Propyne ( C_{3}H_{4} ), Butyne ( C_{4}H_{6} ).
Ans.3. (b)
Two consecutive members of a homologous series differ by a -CH_{2} group.
Ans.4. (c)
The melting and boiling points increase with increasing molecular mass.
Ans.5. (b)
Molecular formula of first member: C_{2}H_{6}O
Molecular formula of second member: C_{3}H_{8})
Molecular formula of third member: C_{4}H_{10}O
Thus, the general formula of the homologous series is C_{n}H_{2n+2}O .
Case Study Question 07
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
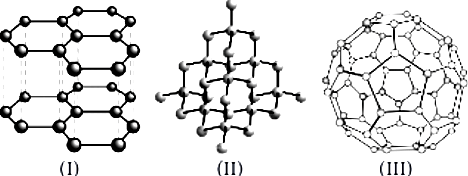
When an element exists in two or more different forms in the same physical state, these different forms are called allotropes and the phenomenon is known as allotropy. Allotropes have similar chemical properties but they differ in their physical properties. Carbon exists in crystalline and amorphous forms. In crystalline form, it occurs as diamond, graphite and fullerenes. Diamond is a colourless, transparent substance having extraordinary brilliance. It is the hardest natural substance known. It is used for cutting marble, granite and glass. Graphite is a greyish-black, opaque substance. It is lighter than diamond i.e., it has lower density. It has sheet like structure having hexagonal layers. One layer slides over the other layer which makes it soft to touch. It is the reason that graphite is used as a lubricant.
Question.1. Substance X is a moderate conductor of electricity. Substance X has the structure shown below: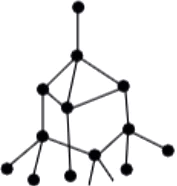
(I) It is a covalent compound.
(II) It has a giant molecular structure.
(III) It has the same structure as graphite.
(IV) It has the same structure as diamond.
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Question.2. Which of the following is correct about the structure of diamond?
(a) Carbon atoms are held together by single covalent bonds.
(b) Electrons move freely through the structure.
(c) Layers of atoms slide easily over each other.
(d) Carbon atoms conduct electricity in the molten state.
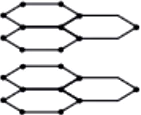
Question.3. Which three allotropes of carbon, do the given figures represent?
Question.4. Identify the incorrect statement(s).
(I) Diamond is the hardest substance known while graphite is smooth and slippery.
(II) Diamond is made up of billions of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral manner to form a giant lattice. All carbon atoms are bonded by strong covalent bonds.
(III) Graphite is a poor conductor of electricity unlike other non-metals.
(IV) Graphite has a giant covalent structure that is made up of layers of carbon atoms. In each layer, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms to form hexagonal rings of carbon atoms.
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) Only (III)
(c) (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Question.5. Structures of two different forms of carbon are given below: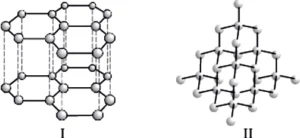
(a) Diamond, Graphite, Isotopes of carbon
(b) Graphite, Diamond, Allotropes of carbon
(c) C^{12} , C^{14} , Allotropes of carbon
(d) C^{14} , C^{12} , Isotopes of carbon
Ans.1. (c)
Each atom is covalently bonded to four other atoms, which in turn, are bonded to four more atoms. Thus, X is a giant molecule and has a structure similar to that of diamond. Substance X is not a compound as it consists of only one type of atoms. Thus, X is an element. Graphite has layers of carbon
atoms.
Ans.2. (a)
Ans.3. (d)
Ans.4. (b)
In graphite only three valence electrons are used for bond formation and hence fourth electron is free to move which makes it a good conductor of electricity.
Ans.5. (b)
Given structures are of graphite and diamond and these are allotropes of carbon.
Case Study Question 08
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
As neutral atom carbon has electronic configuration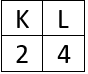
Question.1. Which of the following do not contain a double bond?
I. SO_{2}
II. NH_{3}
III. HCl
IV. O_{2}
(a) I and II only
(b) II and III only
(c) III and IV only
(d) I and IV only
Question.2. Which of the following contains a triple bond?
(a) N_{2}
(b) O_{2}
(c) CO_{2}
(d) H_{2}
Question.3. The shared pair of electrons is said to constitute a bond between two hydrogen atoms.
(a) single
(b) double
(c) triple
(d) ionic
Question.4. Which of the following molecules has all its atoms joined together by double covalent bonds?
(a) Methane
(b) Water
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Nitrogen trichloride
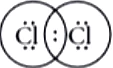
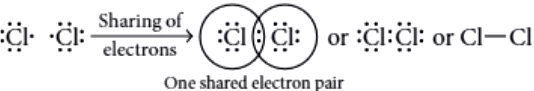
Question.5. Chlorine forms a diatomic molecule, Cl_{2} . The electron dot structure for this molecule is
(a) 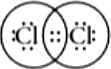

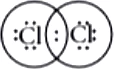
Ans.1. (b)
Both NH_{3} and HCl have single bonds.
Ans.2. (a)
N \equiv N
Ans.3. (a)
Ans.4. (c)
O=C=O
Ans.5. (c)
In chlorine molecule, both chlorine atoms contribute one electron and thus share single electron pair to form single covalent bond. As shared pair is shared by both atoms, they acquire inert gas configuration of argon atom in valence shell.
Case Study Question 09
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
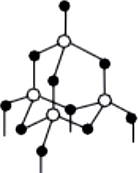
Two allotropic forms of carbon which are crystalline in nature, are diamond and graphite. They differ physically but chemically they are similar. Diamond is the hardest crystalline form of carbon. In diamond, each carbon atom is linked to four other carbon atoms by covalent bonds. In graphite, each carbon atom is linked to three other carbon atoms by covalent bond. Graphite is relatively soft and greasy. It is also a good conductor of electricity. The C-C bond length in graphite is 141.5 pm while in diamond it is 154 pm.
Question.1. Which of the following is a good conductor of heat and electricity?
(a) Coal
(b) Diamond
(c) Charcoal
(d) Graphite
Question.2. Graphite is a good conductor of electricity because
(a) it has free electrons
(b) it has free atoms
(c) it is crystalline
(d) it is soft and greasy
Question.3. Which of the following types of binding forces is present in the structure of diamond?
(a) Ionic
(b) van der Waals’
(c) Covalent
(d) None of these
Question.4. Diamond is not a good conductor of electricity because
(a) it is very hard
(b) its structure is very compact
(c) it is not water soluble
(d) it has no free electron
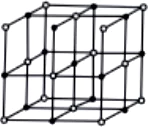
Question.5. Which of the following is the structure of diamond?
(a) 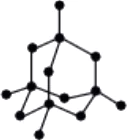
Ans.1. (d)
Ans.2. (a)
Ans.3. (c)
Ans.4. (d)
In diamond, one carbon is attached to four other carbon atoms hence it has no free electron.
Ans.5. (a)
Case Study Question 10
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ from each other in physical or chemical properties are called isomers and the phenomenon is called isomerism. When the isomerism is due to difference in the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, without any reference to space, the phenomenon is called structural isomerism. In other words, structural isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas, i.e., they are different in the order in which different atoms are linked. In these compounds, carbon atoms can be linked together in the form of straight chains, branched chains or even rings.
Question.1. Which of the following sets of compounds have same molecular formula?
(a) Butane and iso-butane
(b) Cyclohexane and hexene
(c) Propanal and propanone
(d) All of these
Question.2. In order to form branching, an organic compound must have a minimum of
(a) four carbon atoms
(b) three carbon atoms
(c) five carbon atoms
(d) any number of carbon atoms
Question.3. Which of the following is an isomeric pair?
(a) Ethane and propane
(b) Ethane and ethene
(c) Propane and butane
(d) Butane and 2-methylpropane
Question.4. Among the following the one having longest chain is
(a) neo-pentane
(b) iso-pentane
(c) 2-methylpentane
(d) 2,2-dimethylbutane
Question.5. The number of isomers of pentane is
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Ans.1. (d)
CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3} ,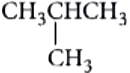
(Butane and iso-Butane-C_{4}H_{10} )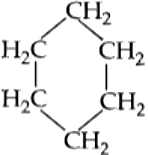
(Cyclohexane and hexene-C_{6}H_{12} )
CH_{3}-CH_{2}-CHO , CH_{3}-CO-CH_{3}
(Propanal and propanone-C_{3}H_{6}O )
Ans.2. (a)
Ans.3. (d)
CH_{3}CH_{2}CH_{2}CH_{3}, and 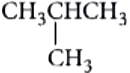
Ans.4. (c)
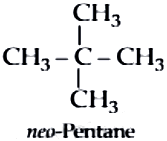
neo-Pentane: 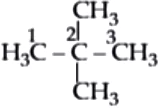
iso-Pentane: 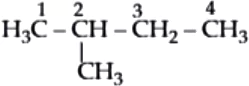
2-Methylpentane: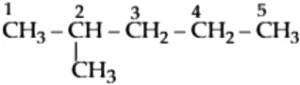
2,2-Dimethylbutane: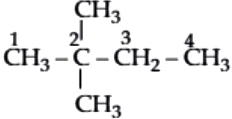
Hence, 2-methylpentane has the longest carbon chain.
Ans.5. (b)
Pentane (C_{5}H_{12} )) has three structural isomers: