Hint: Describe the locations and function of meristematic tissue plants.
Question.1. What property does the meristematic tissue have that results in growth of the plants?
(a) It is a large tissue.
(b) It is a dead tissue.
(c) It is a dividing tissue.
(d) It is a flexible tissue.
Question.2. A student did an experiment to study the role of meristematic tissue in onion roots. For the experiment, an onion was kept in each of the four glasses that were filled with same amount of water.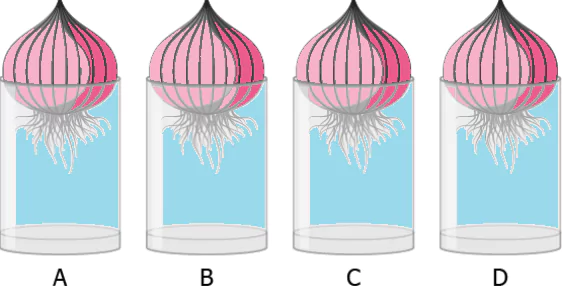
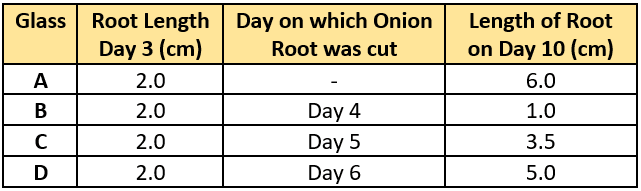
(a) Roots develop meristematic tissue again when cut.
(b) Roots grow faster after meristematic tissue is removed.
(c) Roots stops growing when meristematic tissue is removed.
(d) Roots with and without meristematic tissue had same growth.
Ans.1. (c) It is a dividing tissue.
Ans.2. (c) Roots stops growing when meristematic tissue is removed.
Hint: Classify the meristematic tissue based on their location in the plant body.
Question.3. The image shows the stem of a plant.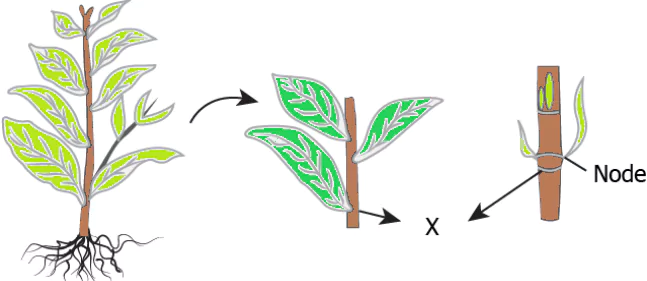
(a) apical meristem
(b) intercalary meristem
(c) lateral meristem
(d) both apical and lateral meristem
Question.4. A student observes that the tree near his house is growing more in width than height. Which tissue is responsible for this type of growth?
(a) apical
(b) intercalary
(c) lateral
(d) both apical and intercalary
Ans.3. (b) intercalary meristem
Ans.4. (c) lateral
Hint: Identify the type of simple permanent tissues and their functions in a plant.
Question.5. The image shows the transverse structure of a sclerenchyma tissue.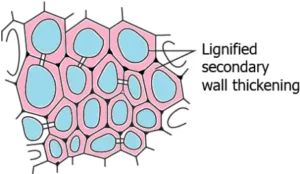
(a) Presence of cells with regular shape
(b) Presence of thin walls and dead cells
(c) Presence of large spaces between the cell
(d) Presence of thick walls and no internal space
Question.6. A class of students were shown a microscopic slide of a permanent tissue in plant for a test.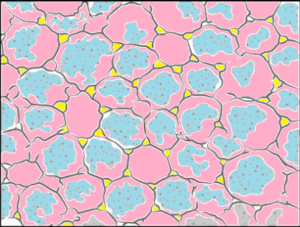
(a) It is aerenchyma tissue as the large air spaces are present.
(b) It is parenchyma tissue as the cells have intercellular spaces and thin walls.
(c) It is sclerenchyma tissue as the cells are thick walled with no internal spacing.
(d) It is collenchyma tissue as the cells are elongated with irregular thick corners.
Ans.5. (d) Presence of thick walls and no internal space
Ans.6. (b) It is parenchyma tissue as the cells have intercellular spaces and thin walls.
Hint: Identify the type of complex permanent and their role in a plant.
Question.7. The image shows the transport of food after photosynthesis in parts of plant from leaves.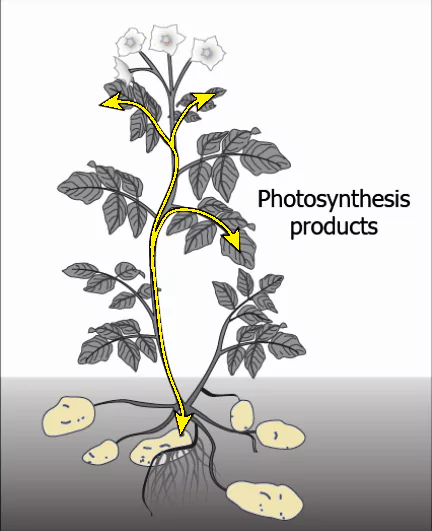
(a) collenchyma
(b) phloem
(c) sclerenchyma
(d) xylem
Question.8. The image shows a setup of an experiment.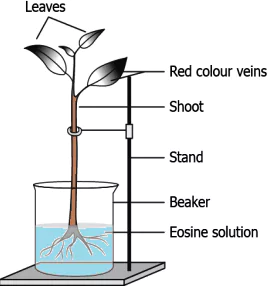
(a) xylem as it helps in the movement of water from roots to stem and leaves
(b) phloem as it helps in the movement of water from roots to stem and leaves
(c) xylem as it helps in the movement of water from leaves to roots and stem
(d) phloem as it helps in movement of water from leaves to roots and stem
Ans.7. (b) phloem
Ans.8. (a) xylem as it helps in the movement of water from roots to stem and leaves
Hint: Classify different animal tissues based on their functions in the body.
Question.9. Which animal tissue acts as a protective tissue of animal’s body?
(a) connective
(b) epithelial
(c) muscular
(d) nervous
Question.10. Muscles that are present in the eye helps the eyelids to blink when dust particles enter the eye. Which animal tissue signals the muscles in the eyelid to blink?
(a) connective tissue
(b) epithelial tissue
(c) muscular tissue
(d) nervous tissue
Ans.9. (b) epithelial
Ans.10. (d) nervous tissue
Hint: Corelate the structure of epithelial tissues to their functions in an organism.
Question.11. Which type of epithelial tissue will help in the movement of particles such as mucus out of the respiratory tract?
(a) 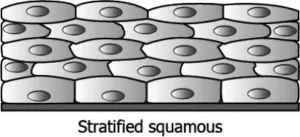
Question.12. Skin is the outermost layer of the body which provide protection from mechanical injuries as well as help in secretion of sweat and oils. Which type of epithelium is the skin likely composed of to facilitate all the mentioned functions?
(a) epithelium having flat surface
(b) epithelium arranged in many layers
(c) epithelium with irregular shaped cells
(d) epithelium with hair-like projections for particle movement
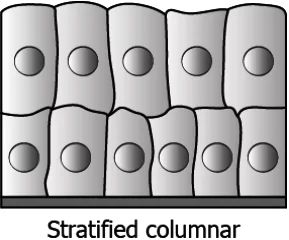
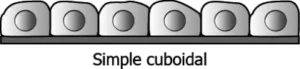
Question.13. The image shows the structure of a specialised epithelium.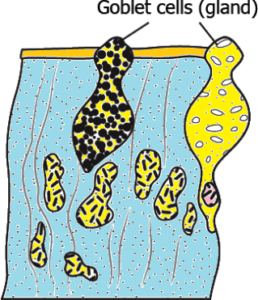
(a) secretion of substances
(b) protection from wear and tear
(c) restrict movement of the tissue
(d) transport of substances across permeable surface
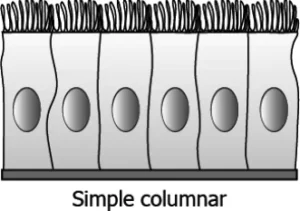
Question.14. The image shows the microscopic view of lung alveoli.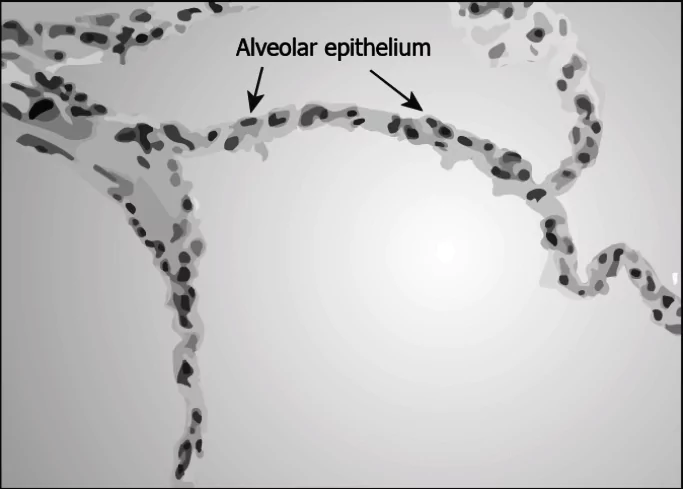
(a) multiple layer of the alveolar cells forms different tissues
(b) single layer of alveolar cells supports easy transport of gases
(c) single layer of alveolar cells provides the protection to the lungs
(d) multiple layer of the alveolar cells facilitates movement of particles
Ans.11. (c) 
Ans.13. (a) secretion of substances
Ans.14. (b) single layer of alveolar cells supports easy transport of gases
Hint: Describe different types of connective tissues and relate their structure to
specific functions.
Question.15. What should be the likely structure of a connective tissue whose framework supports the organs of the body?
(a) multiple layers like the skin
(b) bundle of neurons like nerve
(c) strong and non-flexible like bones
(d) relaxing and contracting like muscles
Question.16. A student studies the structure of areolar connective tissue found in blood vessels.
(a) compact structure of fibers increases the strength
(b) low number of fibers provide rigidity to the structure
(c) loose arrangement of fibers fills the space inside organs and support it
(d) random arrangement of fibers running in same direction provides elasticity
Question.17. The image shows the location of a connective tissue.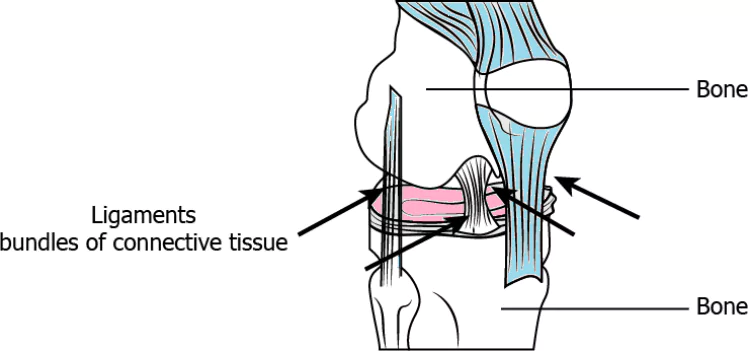
(a) allow bones to move
(b) provides strength to the bones
(c) prevent the bones from bending
(d) connects one bone with the other bones
Question.18. A student observes image of the knee bones of a person who is suffering from a condition called arthritis due to inflammation of joints.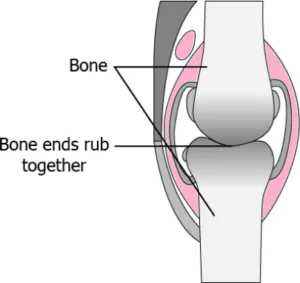
(a) blood as it contains proteins
(b) areolar tissue as it repairs the tissue
(c) ligament as it joins the two bones easily
(d) cartilage as it smoothens surface of the bones
Ans.15. (c) strong and non-flexible like bones
Ans.16. (c) loose arrangement of fibers fills the space inside organs and support it
Ans.17. (d) connects one bone with the other bones
Ans.18. (d) cartilage as it smoothens surface of the bones
Hint: Compare the structure of different types of muscular tissues and relate it to their functions.
Question.19. What is the structure of a muscle that supports voluntary movements of the body?
(a) 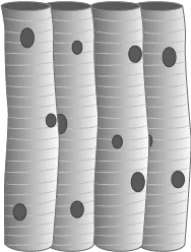
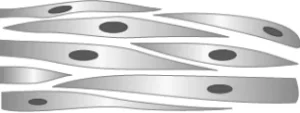
Question.20. The image shows the microscopic view of a type of muscle.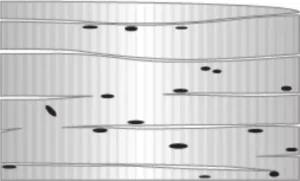
(a) repetitive rows of nuclei with long cells
(b) cylindrical cell with single nucleus in each cell
(c) alternative light and dark coloured cell with branching
(d) alternative bands of light and dark colour with multinucleated cells
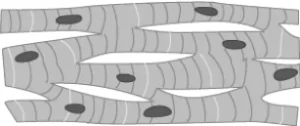
Question.21. The image shows the structure of different types of tissues.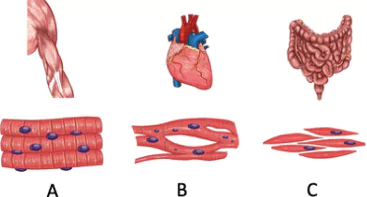
(a) movement of body
(b) rapid movement of iris of the eye
(c) contraction and relaxation of heart
(d) downward movement of food in the alimentary canal
Question.22. The image shows the structure of two type of muscles that are present in two different locations in the human body.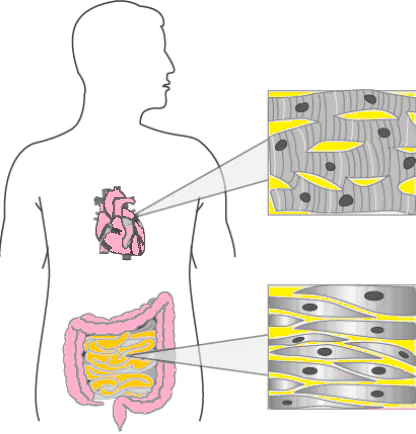
(a) both the muscles protects body organs
(b) both the muscles show voluntary movements
(c) both the muscles helps in movement of body
(d) both the muscles show involuntary movements
Ans.19. (a) 
Ans.21. (c) contraction and relaxation of heart
Ans.22. (d) both the muscles show involuntary movements
Hint: Describe the structure of a neuron and explain the functioning of nervous tissue.
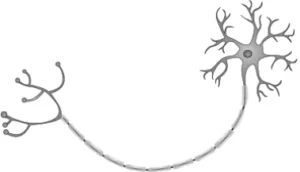
Question.23. The image shows the transfer of nerve impulse to muscles for their movement.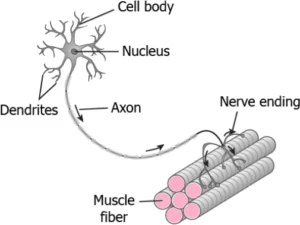
(a) cell body
(b) dendrites
(c) nerve endings
(d) nucleus
Question.24. A person accidently touches a hot plate. What makes the person to move its fore limb away from the hot plate?
(a) smooth muscle
(b) nerve impulse
(c) size of the plate
(d) temperature of the body
Question.25. In case of an injury, the tissue senses the pain. Which statement correctly describe how the nerve impulse will reach the tissue?
(a) From axon of a neuron to the nucleus that are present in the tissue
(b) From cell body of a neuron to the nerve ending that are located on the tissue
(c) From nerve ending of a neuron to the cell body that are present in the neuron
(d) From dendrite of a neuron to the other dendrite that are located on the tissue
Question.26. A student conducts an experiment by applying placing an ice cube on the hands of four different individuals. The student recorded the time they took to respond towards the stimuli by dropping the ice cube.
What can be concluded from the experiment about the function of nervous tissue?
(a) nerve fibers passes signals very fast
(b) nerve impulse depends on the length of the hand
(c) response by nerve fibers depend on duration of the stimuli
(d) different individuals have different types of nervous tissue
Ans.23. (c) nerve endings
Ans.24. (b) nerve impulse
Ans.25. (b) From cell body of a neuron to the nerve ending that are located on the tissue
Ans.26. (a) nerve fibers passes signals very fast