Competency Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Competency Based Questions are new type of questions asked in CBSE Board exam for class 10. Practising the following Competency Based Questions will help the students in facing Board Questions.
Hint: Observe various substances and their physical properties in order to classify them as metals or non-metals.
Question.1. A student performs some activities on two substances and records the observations in a table as shown.
(a) both the substances are metals
(b) both the substances are non-metals
(c) substance M is metal while substance N is non-metal
(d) substance M is non-metal while substance N is metal
Answer. (c) substance M is metal while substance N is non-metal
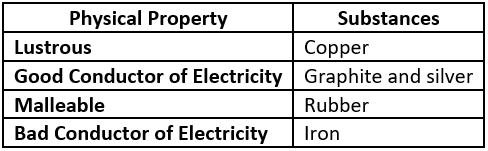
Question.2. Which option classifies the substances based on their physical properties?
(a) 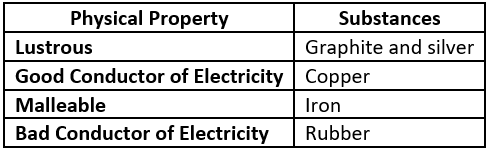
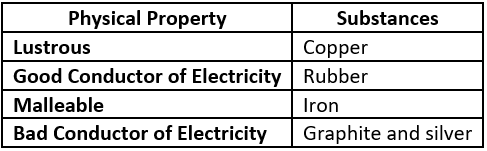
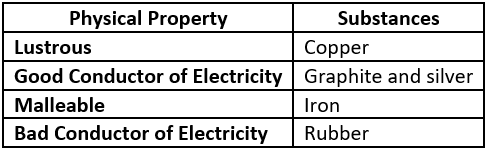
Answer. (c)
Hint: Predict the products when metals & non-metals react with oxygen, water, dilute acids in order to write a balanced chemical equation.
Question.3. An incomplete chemical equation of the reaction between iron and oxygen is shown below:
4Fe(s)+3O_{2} \rightarrow
Which option shows the products formed during the reaction?
(a) 4FeO_{3}(s)
(b) 12FeO(s)
(c) 3Fe_{4}O_{2}(s)
(d) 2Fe_{2}O_{3}(s)
Answer. (d) 2Fe_{2}O_{3}(s)
Question.4. A student writes two incomplete chemical reactions.
X: P_{4}(s)+5O_{2}(g) \rightarrow
Y: 2Mg(s)+O_{2}(g) \rightarrow
Which option completes the reactions to form a balanced chemical equation?
(a) X: P_{5}O_{4}(s) ; Y: (MgO)_{2}(s)
(b) X: 4PO_{10}(s) ; Y: 4MgO(s)
(c) X: P_{4}O_{10}(s) ; Y: 2MgO(s)
(d) X: 5P_{4}O_{2}(s) ; Y: Mg_{2}O_{2}(s)
Answer. (c) X: P_{4}O_{10}(s) ; Y: 2MgO(s)
Hint: Identify the product formed when a metal reacts with a metal salt, in order to list the metals in order of their reactivity.
Question.5. A student studying the chemical properties of metals finds incomplete chemical reactions in his book, as shown:
MgO+HNO_{3} \rightarrow
Which option completes the reaction?
(a) MgO+HNO_{3} \rightarrow Mg_{3}N_{2}+4H_{2}O
(b) MgO+HNO_{3} \rightarrow Mg+NO_{2}+O_{2}
(c) MgO+HNO_{3} \rightarrow Mg(OH)_{2}+2NO_{2}
(d) MgO+HNO_{3} \rightarrow Mg(NO_{3})_{2}+H_{2}O
Answer. (d) MgO+HNO_{3} \rightarrow Mg(NO_{3})_{2}+H_{2}O
Question.6. When hydrochloric acid is added to barium hydroxide, a white-colored compound is formed.
Which option gives the complete chemical reaction?
(a) HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaCl_{2}+2HOH
(b) 2HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaCl_{2}+2HOH
(c) 2HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaH_{2}+2HCl+O_{2}
(d) HCl+2Ba(OH) \rightarrow 2BaCl_{2}+2HOH+O_{2}
Answer. (b) 2HCl+Ba(OH)_{2} \rightarrow BaCl_{2}+2HOH
Question.7. When calcium oxide is added to water, it completely dissolves in water without forming bubbles. What products are formed in this reaction?
(a) Ca and H_{2}
(b) Ca and H_{2}O_{2}
(c) Ca(OH)_{2}
(d) CaH_{2}
Answer. (c) Ca(OH)_{2}
Question.8. A student adds some metallic ash in water taken in a test tube. The ash gets completely dissolved in water and the solution changes colour. What should the student do next to test the chemical properties of the product formed?
(a) Evaporate the solution to get crystals.
(b) Test the basicity using a red litmus paper.
(c) Test the acidity using a blue litmus paper.
(d) Measure the temperature change using a thermometer.
Answer. (b) Test the basicity using a red litmus paper.
Question.9. What happens when a pellet of sodium is dropped in water?
(a) It catches fire and forms oxide.
(b) It absorbs heat and forms oxide.
(c) It catches fire and forms hydroxide.
(d) It absorbs heat and forms hydroxide.
Answer. (c) It catches fire and forms hydroxide.
Question.10. A student drops pieces of potassium and silver in beakers containing water. The image shows the reaction.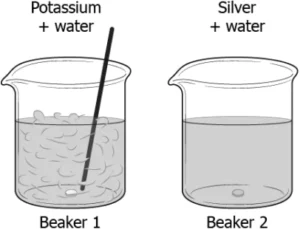
(a) Beaker 1: K_{2}O and H_{2}O ; Beaker 2: AgO and H_{2}O
(b) Beaker 1: KOH and H_{2}O ; Beaker 2: Ag_{2}O and H_{2}O
(c) Beaker 1: K_{2}O and H_{2}O ; Beaker 2: No reaction takes place
(d) Beaker 1: KOH and H_{2}O ; Beaker 2: No reaction takes place
Answer. (b) Beaker 1: KOH and H_{2}O ; Beaker 2: Ag_{2}O and H_{2}O
Question.11. Which product is formed in the chemical reaction between a small trip of magnesium and nitric acid?
(a) MgNO_{3} and 2H_{2}
(b) MgNO_{3} and H_{2}O
(c) Mg(NO_{3})_{2} and 2H_{2}
(d) Mg(NO_{3})_{2} and H_{2}O
Answer. (c) Mg(NO_{3})_{2} and 2H_{2}
Question.12. The chemical reaction between a piece of copper and nitric acid is given by the chemical equations,
Cu+HNO_{3} \rightarrow Cu(NO_{3})_{2}+H_{2}
H_{2}+HNO_{3} \rightarrow H_{2}O+NO_{2}
What can be inferred from the chemical equation?
(a) Copper causes the oxidation of HNO_{3} to form NO_{2} .
(b) Hydrogen gas gets oxidized by HNO_{3} to form water.
(c) gas reacts with oxygen in the air to form water.
(d) Nitrate reacts with hydrogen to form NO_{2} and H_{2}O .
Answer. (b) Hydrogen gas gets oxidized by HNO_{3} to form water.
Hint: Identify the product formed when a metal reacts with a metal salt, in order to list the metals in order of their reactivity.
Question.13. A student writes the chemical equation of the reaction between lead and copper chloride.
Pb(s)+CuCl_{2}(aq) \rightarrow PbCl_{2}(aq)+Cu(s)
Which option explains the reason for the formation of lead chloride?
(a) copper is more reactive than lead
(b) is less reactive than copper
(c) and copper are equally reactive
(d) lead is more reactive than copper
Answer. (d) lead is more reactive than copper
Question.14. A student adds an equal amount of copper sulphate solution in two beakers. He adds zinc in beaker P and silver in beaker Q. The student observes that the color of the solution in beaker P changes while no change is observed in beaker Q. Which option arranges the metals in increasing order of reactivity?
(a) silver-zinc-copper
(b) zinc-copper- silver
(c) silver-copper-zinc
(d) copper-silver-zinc
Answer. (c) silver-copper-zinc
Hint: Discuss the process of how metals react with non-metals, in order to explain formation & properties of ionic compounds.
Question.15. A student learns that sodium and magnesium react with chloride to form sodium chloride and magnesium chloride, as shown.
2Na+Cl_{2} \rightarrow 2NaCl
Mg+Cl_{2} \rightarrow MgCl_{2}
The melting point of sodium chloride is 1074 K while the melting point of magnesium chloride is 981 K. Why does sodium chloride and magnesium chloride have a difference in melting point?
(a) Magnesium chloride is soluble in kerosene and petrol.
(b) Sodium chloride is formed by combining with one molecule of chlorine.
(c) Sodium chloride has strong inter-ionic bonding than magnesium chloride.
(d) chloride is formed by combining only one molecule of magnesium.
Answer. (c) Sodium chloride has strong inter-ionic bonding than magnesium chloride.
Question.16. A student makes an electric circuit using an LED, a battery and connecting wires, as shown.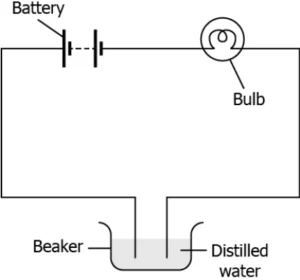
(a) Salt solution is covalent in nature and conducts electricity.
(b) Salt solution has a low melting point which allows the current to flow through it.
(c) Salt solution has a high boiling point which allows the flow of current in the circuit without getting hot.
(d) Salt solution contain ions which makes it conductive and allows the electricity to flow through it.
Answer. (d) Salt solution contain ions which makes it conductive and allows the electricity to flow through it.
Hint: Analyse the process of getting metals from their oxides, sulphides, carbonates in order to extract them from their ores.
Question.17. Which option gives the process of extraction of mercury from its ore cinnabar?
(a) cooling cinnabar in the presence of excess air
(b) cooling cinnabar to convert it into mercuric oxide and then heating it
(c) cinnabar to convert it into mercuric oxide and then heating it again
(d) cinnabar in the presence of limited air to and then adding a small amount of water
Answer. (c) cinnabar to convert it into mercuric oxide and then heating it again
Question.18. A researcher conducts an experiment to obtain zinc from its ore. Which option gives the process that the researcher must perform?
(a) converting metal sulphides into metallic oxides and then using carbon to reduce it to obtain pure metal
(b) metal oxides into metallic sulphides and then using carbon to reduce it to obtain pure metal
(c) converting metal oxides into metallic carbonates and then using carbon to reduce it to obtain pure metal
(d) metallic sulphides into metallic carbonates and then heating to reduce it to obtain pure metal
Answer. (a) converting metal sulphides into metallic oxides and then using carbon to reduce it to obtain pure metal
Hint: Explain the process of electrolytic refining in order to assess how to obtain pure metals from impure samples.
Question.19. The image shows the electrolytic refining of copper. 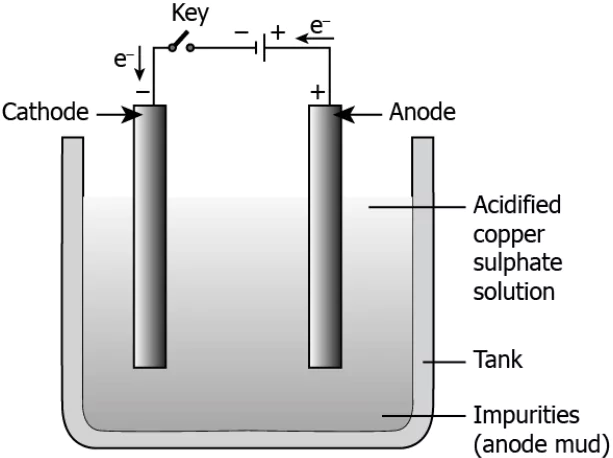
(a) When current is passed, pure copper from anode deposits to the cathode.
(b) When current is passed, pure copper from anode deposits in the electrolytic solution.
(c) When current is passed, pure copper from the electrolytic solution deposits at the anode.
(d) When current is passed, pure copper from the electrolytic solution deposits at the cathode.
Answer. (d) When current is passed, pure copper from the electrolytic solution deposits at the cathode.
Question.20. The table lists the process which explains how pure metals are obtained from impure samples by electrolytic refining.
1. Keep impure metal at anode and pure metal at cathode.
2. Pass current in the electrolytic solution.
3. Insoluble impurities settle in the bottom of the anode as anode mud.
4. Pure metal from anode dissolves in the solution and pure metal from solution deposits on the cathode.
Which option arranges the steps in the appropriate order?
(a) 2-1-3-4
(b) 1-2-4-3
(c) 3-1-4-2
(d) 4-2-3-2
Answer. (b) 1-2-4-3
Hint: Observe corrosion in metalarticles & its process in order to develop ways to prevent corrosion by forming alloys, painting, galvanising.
Question.21. A student notices that the surface of the iron swings in his society playground has turned brown over the years. Which process must be done on the swings to save them from corroding?
(a) putting shades over swings
(b) swings from the playground
(c) covering the surface of the swings with paint
(d) the swings with black paper to protect them from sunlight
Answer. (d) the swings with black paper to protect them from sunlight
Question.22. Earlier, every utensil or tool used at homes was made of iron. The image shows an iron bucket that has deposits of rust over it by using over the years. 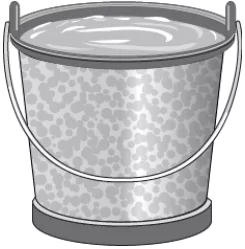
(a) oiling the object after every wash
(b) covering the object with a layer of zinc
(c) cleaning the object with chromium powder regularly
(d) heating and cooling object in cycles to form a thick layer
Answer. (b) covering the object with a layer of zinc