Competency Based Questions Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
Discover our detailed guide on “Competency Based Questions for Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals”! This blog offers comprehensive explanations, practical tips, and structured solutions to help you excel in solving competency-based questions in geometry. Enhance your analytical and problem-solving skills with our expert insights and real-world examples. Perfect for students and educators alike, our guide simplifies complex concepts, making learning effective and enjoyable.
Ready to master Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals? Explore our guide now!
Hint: Apply angle sum property of quadrilateral in order to find the value of the unknown angle.
Question.1. A quadrilateral PKMN is shown below.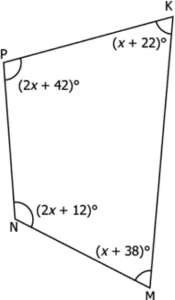
(a) 124°
(b) 104°
(c) 84°
(d) 64°
Question.2. In quadrilateral BDGH, if \angleBDG = 2\angleDGH and \angleBHG = 3\angleHBD, which of the following is true about \angleBDG?
(a) \angleDGH = \frac{1}{3}(360° – 3\angleHBD)
(b) \angleDGH = \frac{1}{2}(360° – 4\angleHBD)
(c) \angleDGH = \frac{1}{3}(360° – 4\angleHBD)
(d) \angleDGH = \frac{1}{2}(360° – 3\angleHBD)
Ans.1. (a) 124°
Ans.2. (a) \angleDGH = \frac{1}{3}(360° – 3\angleHBD)
Hint: List the properties of quadrilaterals in order to classify real life objects into different types of Quadrilaterals.
Question.3. Ravi cut two pieces of marble as shown.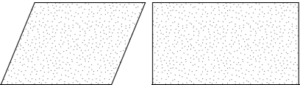
(a) Both are squares.
(b) Both are rhombus.
(c) Both are rectangles.
(d) Both are parallelograms.
Question.4. A clock and a scale are shown below.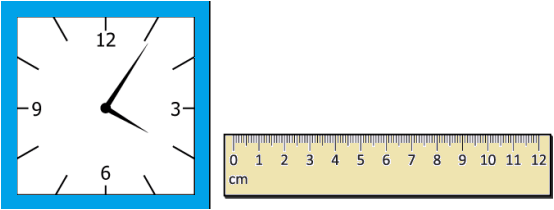
Whose claim is/are correct?
(a) Only Arjun
(b) Only Vinod
(c) Both of them
(d) None of them
Ans.3. (d) Both are parallelograms.
Ans.4. (d) None of them
Hint: List the properties of parallelogram in order to identify if a given quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
Question.5. Which of the following is NOT a property of a quadrilateral that is a parallelogram?
(a) Diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other
(b) A pair of adjacent sides of a quadrilateral is equal
(c) Each pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral is equal
(d) Each pair of opposite angles of a quadrilateral is equal
Question.6. Some quadrilaterals are shown below.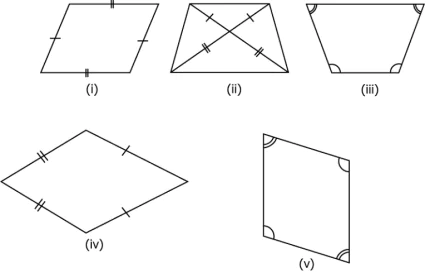
(a) Only i and v
(b) Only i, ii and v
(c) Only ii, iii and iv
(d) Only ii, iv and v
Ans.5. (b) A pair of adjacent sides of a quadrilateral is equal
Ans.6. (a) Only i and v
Hint: Apply properties of parallelogram in order to find
(a) an unknown angle
(b) an unknown side
Question.7. A parallelogram ABCD is shown below.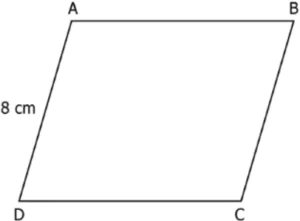
(a) 5 cm
(b) 8 cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) 12 cm
Question.8. In the parallelogram shown below,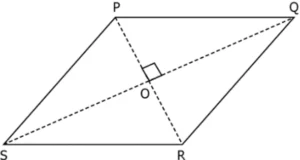
What is the length of the diagonal SQ?
(a) 6 cm
(b) 8 cm
(c) 12 cm
(d) 16 cm
Ans.7. (c) 10 cm
Ans.8. (c) 12 cm
Hint: Prove the midpoint theorem of triangles using concepts of congruency and transversal angles in order to extend the application to quadrilaterals.
Question.9. A figure is shown below where B and D are midpoints of sides MK and MA. 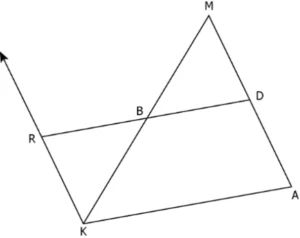
He proves ∆MBD is congruent to ∆KBR by ASA congruency. Which of the following is the next step in the proof of the midpoint theorem?
(a) show that BD = RB
(b) show that BD = BK
(c) show that MB = RK
(d) show that MD = BK
Question.10. In the figure shown, Points N and O are midpoints of sides KL and KM of ∆KLM. 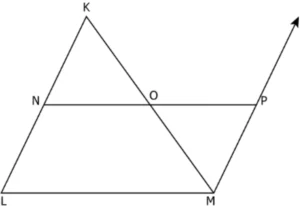
She first proves ∆KON ≅ ∆MOP. Which of the following justifies her step of proof?
(a) ∆KON ≅ ∆MOP by SAS congruency because KO = OM, NO = OP and \angleKON = \angleMOP.
(b) ∆KON ≅ ∆MOP by SAS congruency because KO = OM, KN = MP and \angleNKO = \anglePMO.
(c) ∆KON ≅ ∆MOP by ASA congruency because NO = OP, \angleKON = \angleMOP and \angleNKO = \anglePMO.
(d) ∆KON ≅ ∆MOP by ASA congruency because KO = OM, \angleKON = \angleMOP and \angleNKO = \anglePMO.
Ans.9. (a) show that BD = RB
Ans.10. (d) ∆KON ≅ ∆MOP by ASA congruency because KO = OM, \angleKON = \angleMOP and \angleNKO = \anglePMO.




