NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development
NCERT Solutions for Social Science Class 10 Contemporary India – II Chapter 1 Resources and Development contain the solutions to the In-chapter questions and exercises given in the Geography book – Contemporary India – II. In this chapter, students will mainly find questions related to the resources and development. These NCERT Solutions provide the answers to all questions in a simple and easy-to-understand way. Attempting these answers in the exam will surely help the students in scoring high marks.
NCERT Solutions
Intext Questions
Question.1. Can you identify and name the various items used in making life comfortable in our villages and towns. List the items and name the material used in their making.
Ans.
Villages:
- Clothes: Cotton, synthetic fibers, wool silk, etc
- Furniture: Wood, steel, rubber, etc.
- Houses: Bricks, cement, wood
- Bicycles and motorcycle: Steel, rubber, etc.
Towns:
- Cooking gas stove and cylinder: Steel, brass, rubber, etc.
- Cars and motorcycles: Steel, plastics, brass, etc.
- Fans, room coolers and air conditioners: Steel, copper, plastics, etc.
- Refrigerators and TV sets: Steel, copper, plastics, glass, etc.
Question.2. Identify at least two resources from each category.
Ans. Two resources from each category are identified as follows :
On the Basis of Origin:
- Biotic Resources : human beings, flora, fauna
- Abiotic Resources : Metals, Rocks
On the Basis of Exhaustibility:
- Renewable Resources : Solar Energy, Wind Energy, water, air
- Non-Renewable Resources : coal, petroleum
On the Basis of Ownership:
- Individual Resources : farm, house
- Community Owned Resources : public parks, picnic spots, Playground
- National Resources : forests, wildlife
- International Resources : Marine Resources, Marine Economic Zone, sea routes
On the Basis of the Status of Development:
- Potential Resources : Wind Energy, Geothermal Energy
- Developed Resources : coal, mineral oil
- Stock : water, soil
- Reserves : oil, gas, water stored in dams, forests
Question.3. Prepare a list of stock and reserve, resources that you are familiar with from your local area.
Ans.
Stock : Gases, wind energy, geothermal energy, solar energy, water etc.
Reserves : Water dams, woods from forests, oil refineries, water of rivers, forests etc.
Question.4. Imagine, if the oil supply gets exhausted one day, how would this affect our life style?
Ans.
- The transport system will be greatly affected.
- Students will have to use foot or cycle to go to school.
- People will not be able to reach their office and other places on time.
- The price of vegetables and all items of daily use will increase.
- It will take more time and difficulty in transporting the goods from one place to another.
Question.5. Plan a survey in your colony/village to investigate people’s attitude towards recycling of the domestic/agricultural wastes. Ask questions about:
(a) What do they think about resources they use?
(b) What is their opinion about the wastes, and its utilisation?
(c) Collage your results.
Ans. (a) They think about the resources used by them, that in any way, they should use their resources in a balanced and economical way only when they are needed so that those people can fulfill their needs and do not exploit them so that their availability and use is expected to be maintained in future.
(b) People believe that instead of disposing waste in a systematic way, it is appropriate to use it in different ways, like the best way to destroy waste is to make fertilizer from it. Large pits are filled with waste and buried with soil.
Within a few days, this waste decomposes and becomes ready in the form of compost.
(c) Students should do this work themselves in their own class with the help of teacher.
Question.6. Prepare a list of resources found in your state and also identify the resources that are important but deficit in your state.
Ans. I am a student of Rewa, Madhya Pradesh.
The resources found more in Madhya Pradesh are
(i) diamond,
(ii) limestone,
(iii) coal,
(iv) manganese ore,
(v) bauxite,
(vi) copper ore,
(vii) fire clay,
(viii) human resources,
(ix) livestock
(x) slate pyrophyllite-diaspore etc.
Resources found in small quantities in Madhya Pradesh are as follows:
(i) iron,
(ii) natural gas,
(iii) petroleum etc.
Question.7. Can you name some resource rich but economically backward regions and some resource poor but economically developed regions? Give reasons for such a situation.
Ans. States of Orissa, Assam, and Jharkhand are rich in resources but are economically backward.
States of Punjab, Delhi, and Haryana are poor in resources but are economically developed.
Question.8. Try to do a comparison between the two pie charts given for land use and find out why the net sown area and the land under forests have changed from 1960-61 to 2014-15 very marginally.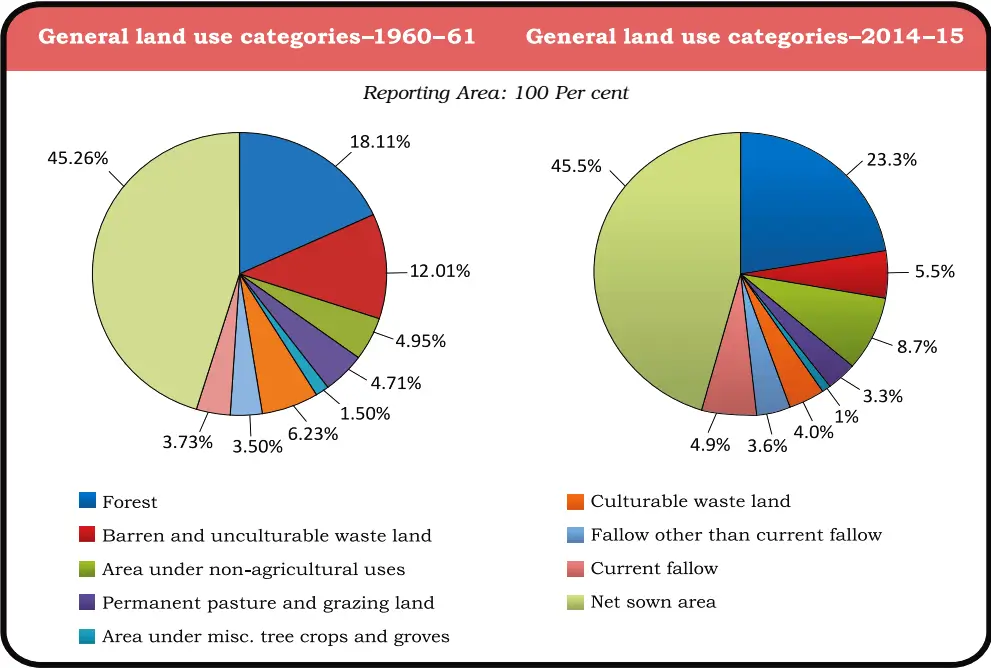
- Urbanization
- floods
- Increasing population,
- Fragmentation of land holdings
- Declining water table
- Unabated and massive conversion of agricultural land for building houses and construction of infrastructure.
- Rise in cost of irrigation
Question.9. The pattern of net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman Nicobar Islands. Find out reasons for the low proportion of net sown area in these states.
Ans. Net sown area in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram and Manipur is low mainly due to the hilly and rocky terrain. Andaman and Nicobar Islands are covered by dense tropical forests and so net sown area is low.
TEXTBOOK EXERCISE
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question.1. Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(A) Intensive cultivation
(B) Deforestation
(C) Over irrigation
(D) Overgrazing
Ans. (C) Over irrigation
Question.2. In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practised?
(A) Punjab
(B) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(C) Haryana
(D) Uttarakhand
Ans. (D) Uttarakhand
Question.3. In which of the following states black soil is predominantly found?
(A) Uttar Pradesh
(B) Maharashtra
(C) Rajasthan
(D) Jharkhand
Ans. (B) Maharashtra
II. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
Question.1. Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
Ans. The three states having black soil are –
- Maharashtra
- Gujarat
- Madhya Pradesh
The crop grown in black soil is cotton.
Question.2. What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Ans. The type of soil found in river deltas of the eastern coast is Alluvial Soil.
Following are the three main features of Alluvial soil –
- Very fertile hence good for cultivation of crops
- Consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay
- It has a good quantity of potash, lime, phosphoric acid which is good for the growth of paddy and sugarcane
Question.3. What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Ans. The main techniques that can be used to control soil erosion in the hilly areas are given below-
- Contour ploughing
- Terrace farming
- Strips of grass are allowed to grow between the crops, this method is known as strip cropping.
III. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
Question.1. Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
Ans. The use of land is determined both by physical factors such as topography, climate, soil types as well as human factors such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc. The pattern of the net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman Nicobar Islands. Forest area in the country is far lower than the desired 33 per cent of geographical area, as it was outlined in the National Forest Policy (1952). It was considered essential for the maintenance of the ecological balance. A part of the land is termed as wasteland and land put to other non-agricultural uses. Wasteland includes rocky, arid and desert areas and land put to other non-agricultural uses includes settlements, roads, railways, industry etc. Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it has resulted in land degradation.
Question.2. How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Ans.
- Large scale production leads to over utilization of resources as more and more raw sources are required.
- Technological advancement led to greater exploitation of resources.
- Technological development results in economic development.
- Therefore, the needs of the people are increased equally, which led to more consumption of resources.
- In developed nations the needs of the people are very high.
- Improved medical and health resources led to huge consumption of resources.
- Introduction of more developed machineries.
Project/Activity
Question.1. Make a project showing consumption and conservation of resources in your locality.
Ans. Students can do this project on their own as per the guidelines given by their teacher.
Question.2. Have a discussion in the class– how to conserve various resources used in your school.
Ans. In the presence of the teacher in your class at school, discuss the topic given in the question amongst themselves.
Question.3. Imagine if oil supplies get exhausted, how will this affect our life style?
Ans.
- If oil supplies get exhausted, this will affect our life-style very much because in such a situation the machines, vehicles, railways etc. will not be able to run.
- People would not be able to go from one place to another because oil is needed for every means of transport.
- Most of our activities are depended on petroleum products like petrol, diesel, LPG, CNG etc.
Question.4. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
(i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
(ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
(iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
(iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
(i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
(ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
(iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
(iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
(v) Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
(vi) The Great Plains of India are made up of these soils.
Ans. 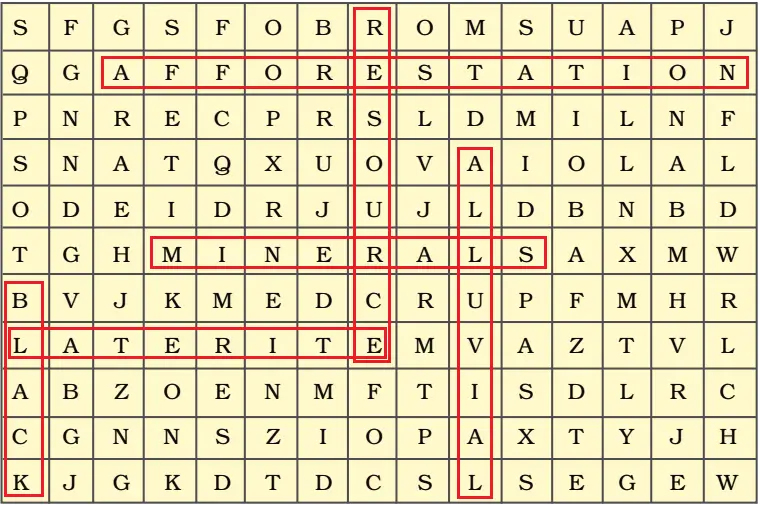
(ii) Minerals
(iii) Black
(iv) Laterite
(v) Afforestation
(vi) Alluvial