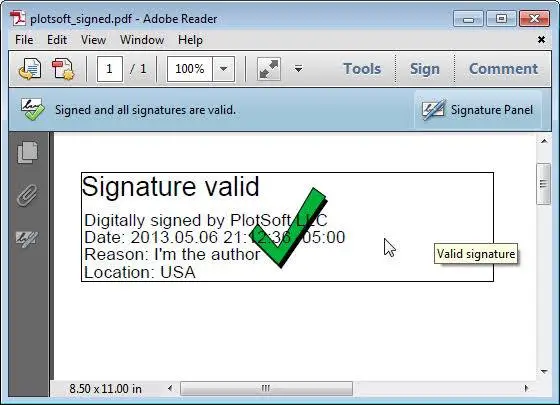
What is Digital Signature?
A digital signature is a cryptographic technique used to verify the authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation of digital documents or messages. It provides a way to ensure that a digital document or message has not been tampered with during transmission and that it originated from the expected sender.
Here’s how digital signatures work:
Hashing
The first step in creating a digital signature is to generate a unique hash value for the document or message. A hash function takes the input data and produces a fixed-size string of characters, called a hash value or message digest. Even a small change in the input data will result in a significantly different hash value.
Private Key Encryption
The hash value is then encrypted using the sender’s private key. The private key is a part of a cryptographic key pair, consisting of a private key and a corresponding public key. The private key is kept secret and known only to the sender.
Digital Signature
The encrypted hash value, along with the original document or message, forms the digital signature. It is appended to the document or message and can be transmitted along with it.
Verification
To verify the digital signature, the recipient uses the sender’s public key to decrypt the encrypted hash value. If the decrypted hash value matches the hash value computed from the received document or message, it indicates that the document or message has not been altered during transmission and that it originated from the expected sender.
Digital signatures provide several benefits:
Authentication
Digital signatures provide proof of the identity of the sender. The recipient can verify the signature using the sender’s public key, ensuring that the document or message was signed by the claimed sender.
Integrity
Any modification to the signed document or message, intentional or accidental, will result in a different hash value, rendering the signature invalid. Thus, digital signatures protect the integrity of the data by detecting any changes made.
Non-repudiation
Digital signatures provide non-repudiation, which means that the sender cannot deny sending the document or message. Since the signature can only be created with the sender’s private key, it serves as evidence of the sender’s intent.
Tamper Detection
If someone tries to tamper with the document or message during transmission, the signature verification will fail, indicating that the data has been altered.
Digital signatures are widely used in various applications, such as secure email communication, software distribution, financial transactions, contracts, and legal documents. They play a crucial role in ensuring the security and authenticity of digital communications and transactions.
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर क्या है?
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर एक क्रिप्टोग्राफ़िक तकनीक है जिसका उपयोग डिजिटल दस्तावेज़ों या संदेशों की प्रामाणिकता, अखंडता और गैर-अस्वीकरण को सत्यापित करने के लिए किया जाता है। यह यह सुनिश्चित करने का एक तरीका प्रदान करता है कि ट्रांसमिशन के दौरान किसी डिजिटल दस्तावेज़ या संदेश के साथ छेड़छाड़ नहीं की गई है और यह अपेक्षित प्रेषक से उत्पन्न हुआ है।
यहां बताया गया है कि डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर कैसे काम करते हैं:
हैशिंग
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर बनाने में पहला कदम दस्तावेज़ या संदेश के लिए एक अद्वितीय हैश मान उत्पन्न करना है। एक हैश फ़ंक्शन इनपुट डेटा लेता है और वर्णों की एक निश्चित आकार की स्ट्रिंग उत्पन्न करता है, जिसे हैश मान या संदेश डाइजेस्ट कहा जाता है। यहां तक कि इनपुट डेटा में एक छोटे से बदलाव के परिणामस्वरूप भी काफी भिन्न हैश मान प्राप्त होगा।
निजी कुंजी एन्क्रिप्शन
फिर हैश मान को प्रेषक की निजी कुंजी का उपयोग करके एन्क्रिप्ट किया जाता है। निजी कुंजी एक क्रिप्टोग्राफ़िक कुंजी जोड़ी का एक हिस्सा है, जिसमें एक निजी कुंजी और संबंधित सार्वजनिक कुंजी शामिल होती है। निजी कुंजी गुप्त रखी जाती है और केवल प्रेषक को ही ज्ञात होती है।
अंगुली का हस्ताक्षर
एन्क्रिप्टेड हैश मान, मूल दस्तावेज़ या संदेश के साथ, डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर बनाता है। इसे दस्तावेज़ या संदेश के साथ जोड़ा जाता है और इसके साथ प्रसारित किया जा सकता है।
सत्यापन
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर को सत्यापित करने के लिए, प्राप्तकर्ता एन्क्रिप्टेड हैश मान को डिक्रिप्ट करने के लिए प्रेषक की सार्वजनिक कुंजी का उपयोग करता है। यदि डिक्रिप्टेड हैश मान प्राप्त दस्तावेज़ या संदेश से गणना किए गए हैश मान से मेल खाता है, तो यह इंगित करता है कि दस्तावेज़ या संदेश ट्रांसमिशन के दौरान बदला नहीं गया है और यह अपेक्षित प्रेषक से उत्पन्न हुआ है।
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर कई लाभ प्रदान करते हैं:
प्रमाणीकरण
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर प्रेषक की पहचान का प्रमाण प्रदान करते हैं। प्राप्तकर्ता प्रेषक की सार्वजनिक कुंजी का उपयोग करके हस्ताक्षर को सत्यापित कर सकता है, यह सुनिश्चित करते हुए कि दस्तावेज़ या संदेश पर दावा किए गए प्रेषक द्वारा हस्ताक्षर किए गए थे।
अखंडता
हस्ताक्षरित दस्तावेज़ या संदेश में कोई भी संशोधन, जानबूझकर या आकस्मिक, के परिणामस्वरूप एक अलग हैश मान होगा, जिससे हस्ताक्षर अमान्य हो जाएगा। इस प्रकार, डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर किए गए किसी भी परिवर्तन का पता लगाकर डेटा की अखंडता की रक्षा करते हैं।
गैर परित्याग
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर गैर-अस्वीकृति प्रदान करते हैं, जिसका अर्थ है कि प्रेषक दस्तावेज़ या संदेश भेजने से इनकार नहीं कर सकता है। चूँकि हस्ताक्षर केवल प्रेषक की निजी कुंजी से ही बनाया जा सकता है, यह प्रेषक के इरादे के प्रमाण के रूप में कार्य करता है।
छेड़छाड़ का पता लगाना
यदि कोई ट्रांसमिशन के दौरान दस्तावेज़ या संदेश के साथ छेड़छाड़ करने की कोशिश करता है, तो हस्ताक्षर सत्यापन विफल हो जाएगा, यह दर्शाता है कि डेटा बदल दिया गया है।
डिजिटल हस्ताक्षर व्यापक रूप से विभिन्न अनुप्रयोगों में उपयोग किए जाते हैं, जैसे सुरक्षित ईमेल संचार, सॉफ़्टवेयर वितरण, वित्तीय लेनदेन, अनुबंध और कानूनी दस्तावेज़। वे डिजिटल संचार और लेनदेन की सुरक्षा और प्रामाणिकता सुनिश्चित करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाते हैं।