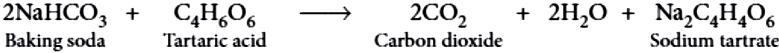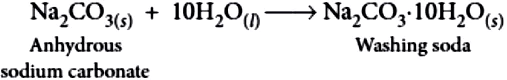Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts
Welcome to our detailed guide on Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2: Acids, Bases, and Salts! This blog is specially designed to help you navigate through the complexities of acids, bases, and salts with ease and confidence. Case study questions are essential for developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills in chemistry, and our guide provides comprehensive explanations and practical tips to tackle these questions effectively. Whether you’re a student aiming for academic excellence or a teacher seeking valuable resources, our guide on case study questions offers structured solutions, expert insights, and real-world examples to enhance your understanding.
Ready to master the art of solving case study questions? Dive in and explore our essential tips and strategies!
Case Study Question 01
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces CO_{2} on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. Sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter. Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder. When baking powder is heated, NaHCO_{3} decomposes to give CO_{2} , which makes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of sodium tartrate.
Question.1. On passing excess CO_{2} gas in aqueous solution of sodium carbonate, the substance obtained is
(a) NaOH
(b) NaHCO_{3}
(c) Na_{2}CO_{3}\cdot 10H_{2}O
(d) Na_{2}CO_{3}\cdot H_{2}O
Question.2. When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid, it evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved?
(I) It turns lime water milky.
(II) It extinguishes a burning splinter.
(III) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide.
(IV) It has a pungent odour.
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (I), (II) and (III)
(c) (II), (III) and (IV)
(d) (I) and (IV)
Question.3. Select the correct statement regarding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(a) CO and CO_{2} are produced during the heating of NaHCO_{3} .
(b) It is insoluble in water.
(c) It is used in soda-acid fire extinguishers.
(d) All of these.
Question.4. Acetic acid was added to a solid X kept in a test tube. A colourless and odourless gas was evolved. The gas was passed through lime water which turned milky. It was concluded that
(a) solid X is sodium hydroxide and the gas evolved is CO_{2}
(b) solid X is sodium bicarbonate and the gas evolved is CO_{2}
(c) solid X is sodium acetate and the gas evolved is CO_{2}
(d) solid X is sodium chloride and the gas evolved is CO_{2} .
Question.5. Which of the following statements are correct regarding baking soda?
(I) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(II) On heating, baking soda gives sodium carbonate.
(III) It is used for manufacture of soap.
(IV) It is an ingredient of baking powder.
(a) I and IV only
(c) I, II and IV only
(b) I, II and III only
(d) I, II, III and IV
Ans.1. (b)
Na_{2}CO_{3}+H_{2}O+CO_{2} \rightarrow 2NaHCO_{3}
Ans.2. (b)
NaHCO_{3}+CH_{3}COOH \rightarrow CH_{3}COONa+CO_{2}(\uparrow)+H_{2}O
Carbon dioxide gas is evolved which turns limewater milky. It extinguishes a burning splinter since it is not a supporter of combustion. It dissolves in sodium hydroxide solution and it is an odourless gas.
Ans.3. (c)
2NaHCO_{3}+Heat \rightarrow Na_{2}CO_{3}+H_{2}O+CO_{2}
NaHCO_{3} is soluble in water.
Ans.4. (b)
NaHCO_{3}+CH_{3}COOH \rightarrow CH_{3}COONa+CO_{2}(\uparrow)+H_{2}O
Ans.5. (c)
It is not used in manufacture of soap.
Case Study Question 02
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
Bleaching powder is also known as chloride of lime. It is a solid and yellowish white in colour. Bleaching powder can be easily identified by the strong smell of chlorine. When calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) reacts with chlorine, it gives calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder) and water is formed. Aqueous solution of bleaching powder is basic in nature. The material to be bleached is first passed through solution of NaOH to remove greasy matter. Then it is passed through aqueous solution of bleaching powder and very dil. HCl solution. HCl reacts with bleaching powder to liberate nascent oxygen which bleaches material.
Question.1. Bleaching powder is used as
(a) bleaching agent in textile, paper and jute industry
(b) disinfectant for water to make water free of germs
(c) oxidising agent in many industries
(d) all of these.
Question.2. Bleaching powder is also known as
(a) calcium oxychloride
(b) calcium hypochlorite
(c) chloride of lime
(d) all of these.
Question.3. Bleaching powder gives smell of chlorine because it
(a) is unstable
(b) gives chlorine on exposure to atmosphere
(c) is a mixture of chlorine and slaked lime
(d) contains excess of chlorine.
Question.4. Select the correct statement(s) regarding bleaching powder.
(a) It is pale yellow powder having smell of chlorine.
(b) It is sparingly soluble in water and gives milky suspension when dissolved in water.
(c) As bleaching powder gives nascent oxygen, it shows bleaching property.
(d) All of these.
Question.5. Identify the product ‘X’ in the given reaction.
Ca(OH)_{2}+Cl_{2} \rightarrow X +H_{2}O
(a) CaOCl_{2}
(b) CaCl_{2}
(c) Ca\left(ClO_{3}\right)_{2}
(d) CaCO_{3}
Ans.1. (d)
Ans.2. (d)
Ans.3. (b)
Bleaching powder gives chlorine on exposure to air by reacting with CO_{2} .
CaOCl_{2}+CO_{2} \rightarrow CaCO_{3}+Cl_{2}
Ans.4. (d)
Ans.5. (a)
Ca(OH)_{2}+Cl_{2} \rightarrow CaOCl_{2}+H_{2}O
Case Study Question 03
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
The preparation of washing soda is carried out through following steps:
Step-I: Manufacture of sodium hydrogen carbonate: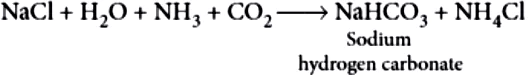
2NaHCO_{3(s)} \rightarrow Na_{2}CO_{3(s)}+CO_{2(g)}+H_{2}O_{(g)}
Step-III: Recrystallisation of sodium carbonate : Sodium carbonate thus obtained is re-crystallised to form crystals of washing soda.
Question.1. Some of the uses of washing soda are given below:
(I) It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
(II) It is used in glass industry.
(III) It is used in paper industry.
(IV) It is used in the manufacture of sodium compounds such as borax.
Select the correct option regarding uses of washing soda.
(a) (1) and (II) only
(c) (II) and (IV) only
(b) (II) and (III) only
(d) (I), (II), (III) and (IV)
Question.2. What products will be formed alongwith water when sodium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid?
(a) CO and NaCl
(b) Na and CO_{2}
(c) NaCl and CO_{2}
(d) Na and CO
Question.3. Chief raw materials for the manufacture of washing soda are
(a) sodium chloride, ammonia and limestone
(b) ammonia, sodium hydrogen carbonate and copper sulphate
(c) sodium hydroxide, calcium chloride and ammonia
(d) calcium chloride, sodium chloride and copper sulphate.
Question.4. What is the action of sodium carbonate on litmus paper?
(a) Turns red litmus blue
(b) Turns blue litmus red
(c) No change on litmus
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Question.5. What products will be obtained when solution of sodium carbonate and slaked lime is heated?
(a) NaOH and CaCl_{2}
(b) CaCO_{3} and NaOH
(c) NaHCO_{3} and NaOH
(d) NaCl and CaCO_{3}
Ans.1. (d)
Ans.2. (c)
Na_{2}CO_{3} reacts with dilute acids to give CO_{2} gas with brisk effervescence. 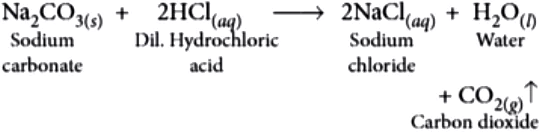
Chief raw materials for the manufacture of washing soda are sodium chloride (NaCl), ammonia ( NH_{3} ) and limestone ( CaCO_{3} ).
Ans.4. (a)
Sodium carbonate turns red litmus blue.
Ans.5. (b)
Sodium hydroxide and calcium carbonate are formed when the solution of sodium carbonate and slaked lime, Ca(OH)_{2} is heated.
Na_{2}CO_{3}+Ca(OH)_{2} \rightarrow 2NaOH+CaCO_{3}
Case Study Question 04
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
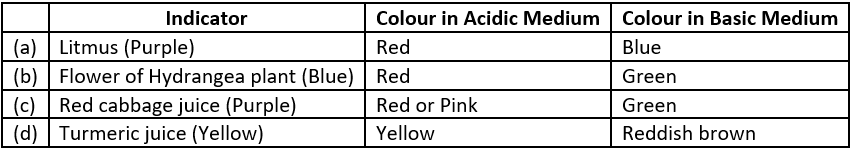
“Indicator is a chemical compound which is added to the solution in very small amount to detect its acidic or basic nature.” As they show colour change in acidic and basic medium, they are also called acid-base indicators. In other words, “an acid-base indicator is that substance which possesses one colour in acidic medium and a different colour in alkaline medium.”
Indicators, basically, are coloured organic substances either extracted from plants (natural indicators) or synthesised in the laboratory (synthetic indicators). A few common acid base indicators are: Litmus, phenolphthalein, methyl orange etc. In addition to these there are some naturally occurring substances which have different smell in acidic and basic medium. These substances are called olfactory indicators.
Question.1. Which one of the following will turn red litmus blue?
(a) Vinegar
(b) Baking soda solution
(c) Lemon juice
(d) Soft drinks
Question.2. A solution turns blue litmus red. The pH of the solution is probably
(a) 8
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 6
Question.3. A solution in test tube ‘A’ turns red litmus blue, evolves hydrogen gas on reaction with zinc and does not react with sodium carbonate. Whereas, solution in test tube ‘B’ turns blue litmus red, liberates hydrogen gas on reaction with zinc and evolves carbon dioxide gas with sodium carbonate. Identify ‘A’ and ‘B.
(a) ‘A’ is an acid, ‘B’ is a base.
(b) ‘A’ is a base, ‘B’ is an acid.
(c) Both ‘A’ and ‘B’ are bases.
(d) Both ‘A’ and ‘B’ are acids.
Question.4. Select the incorrect option.
Question.5. Which one of the following can be used as an acid-base indicator by visually impaired student?
(a) Litmus
(b) Turmeric
(c) Vanilla essence
(d) Methyl orange
Ans.1. (b)
Baking soda ( NaHCO_{3} ) is basic in nature.
Ans.2. (d)
The solution turns blue litmus red, hence it is acidic.
Ans.3. (b)
Acids turn blue litmus red, liberate hydrogen gas with zinc and evolve carbon dioxide gas with metal carbonates. Bases turn red litmus blue, evolve hydrogen gas with zinc and do not react with metal carbonates.
Ans.4. (b) 
Vanilla essence is an olfactory indicator. So, its smell is different in acidic and basic medium which can be detected easily by a visually impaired student.
Case Study Question 05
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
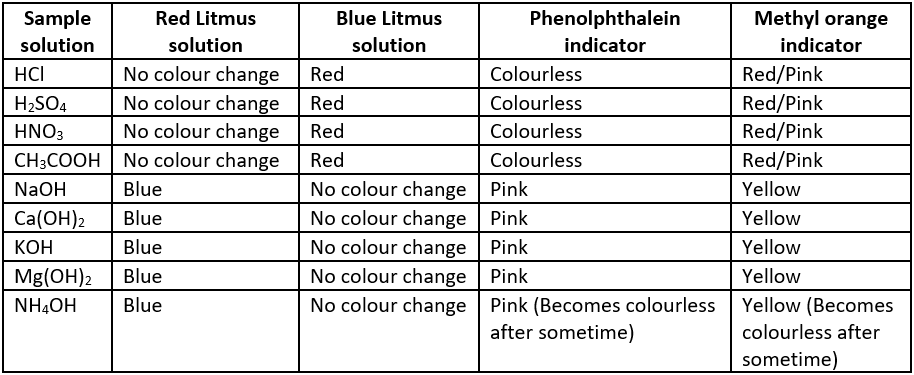
Acids turn blue litmus red but have no effect on red litmus. Bases turn red litmus blue but have no effect on blue litmus. The sample in which phenolphthalein remains colourless while methyl orange changes to pink/ red are acids while the samples in which phenolphthalein colour changes to pink and methyl orange changes to yellow are bases. Some observations of different sample solutions in litmus, phenolphthalein and methyl orange indicator are given in the table.
Question.1. Which of the following substances does not turn red litmus solution to blue?
(a) Al(OH)_{3}
(b) Mg(OH)_{2}
(c) H_{3}PO_{4}
(d) NH_{4}OH
Question.2. Phenolphthalein’s colour in basic medium is ______ but in acid it is ______.
(a) pink, colourless
(b) yellow, pink
(c) pink, orange
(d) blue, red
Question.3. Which of the following acids are edible?
(I) Citric acid
(II) Tartaric acid
(III) Hydrochloric acid
(IV) Carbonic acid
(a) (I) and (II) only
(b) (I), (II) and (IV) only
(c) (I), (II) and (III) only
(d) (I), (II), (III) and (IV)
Question.4. The colour of methyl orange in neutral solution is
(a) red
(b) orange
(c) yellow
(d) purple.
Question.5. Which of the following cannot act as an indicator?
(a) Methyl orange
(b) Methyl chloride
(c) Turmeric juice
(d) Phenolphthalein
Ans.1. (c)
Ans.2. (a)
Ans.3. (b)
Citric and tartaric acid are from organic substances such as lemon and tamarind respectively and they are edible. Hydrochloric acid though formed inside stomach is not edible. Carbonic acid is a mild acid and is edible in the form of soda water.
Ans.4. (b)
Ans.5. (b)
Case Study Question 06
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
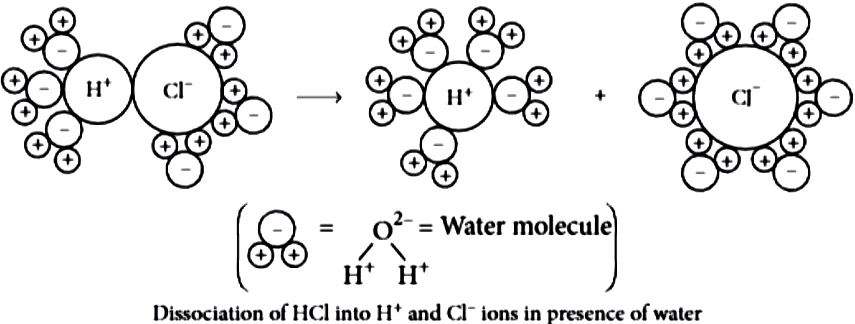
The acidic behaviour of acids is due to the presence of hydrogen( H^{+} ) ions in them. They produce hydrogen ions in the presence of water. Water is a polar solvent and this property of water helps in weakening the bond between the ions and makes them soluble. Hence, acids and bases produce ions in aqueous solutions.
It may be noted that a dry HCl gas or a solution of hydrogen chloride in organic, non- polar solvents like toluene or benzene do not show acidic properties. This is because hydrogen chloride does not undergo ionization in toluene.
The reason why HCl splits into H^{+} and Cl^{-} ions in presence of water lies in the fact that water molecules, being polar, pull the H^{+} and Cl^{-} ions apart and thus, the bond in HCl is broken.
Question.1. Identify the wrong statement.
(a) Higher the hydronium ion concentration, lower is the pH value.
(b) Universal indicator is used to judge how strong a given acid or base is.
(c) As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents increase in H^{+} ion concentration in the solution.
(d) Value less than 7 on the pH scale represents an acidic solution.
Question.2. If the pH of a solution is 8, then its H^{+} ion is
(a) log 10^{-8}
(b) 10^{8}
(c) 10^{-8}
(d) 8
Question.3. In terms of acidic strength, which one of the following is in the correct increasing order?
(a) Water < Acetic acid < Hydrochloric acid
(b) Water < Hydrochloric acid < Acetic acid
(c) Acetic acid < Water < Hydrochloric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid < Water < Acetic acid
Question.4. Which of the following compounds does not give H^{+} ions in aqueous solution?
(a) H_{3}PO_{4}
(b) C_{2}H_{5}OH
(c) H_{2}CO_{3}
(d) CH_{3}COOH
Question.5. Four solutions labelled as P, Q, R and S have pH values 1, 9, 3 and 13 respectively. Which of the following statements about the given solutions is incorrect?
(a) Solution P has higher concentration of hydrogen ions than solution R.
(b) Solution Q has lower concentration of hydroxide ions than solution S.
(c) Solutions P and Q will turn red litmus solution blue.
(d) Solution P is highly acidic while solution Q is weakly basic.
Ans.1. (c)
As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents decrease in H^{+} ion concentration in the solution.
Ans.2. (c)
pH= \log_{10}[H^{+}] = 8
⇒ \log_{10}[H^{+}] = -8
⇒ [H^{+}] = 10^{-8} mol/L
Ans.3. (a)
Ans.4. (b)
C_{2}H_{5}OH is not an ionic compound, it is a covalent compound and hence does not give H+ ions in aqueous solution.
Ans.5. (c)
(a) Lower the pH of the solution, more acidic is the solution and higher is the [H^{+}] ions.
Thus, solution P (pH = 1) has higher [H^{+}] ions than solution R (pH = 3).
(b) Higher the pH of the solution, more basic is the solution and higher is the [OH^{-}] ions.
Thus, solution Q (pH = 9) has lower [OH^{-}] ions than solution S (pH = 13).
(c) Solution P (pH = 1) is acidic which turns blue litmus solution red whereas solution Q (pH = 9) is basic which turns red litmus solution blue.
(d) Solution P (pH = 1) is highly acidic while solution S (pH = 13) is highly basic and solution Q (pH = 9) is weakly basic.
Case Study Question 07
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
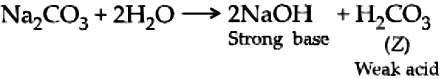
A compound, X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacids. When heated it gives a compound, Y which is anhydrous and absorbs water to become a hydrated salt. When this salt is kept in open air, it loses water molecules in a process called efflorescence. When dissolved in water it forms a strong base and a weak acid, Z.
Question.1. What is the compound, X?
(a) NaHCO_{3}
(b) Na_{2}CO_{3}
(c) NaOH
(d) NaCl
Question.2. The compound, Y is
(a) NaHCO_{3}
(b) Na_{2}CO_{3}
(c) Na_{2}CO_{3}\cdot 10H_{2}O
(d) NaCl
Question.3. What is the nature of the solution formed by dissolving Y in water?
(a) Alkaline
(b) Acidic
(c) Neutral
(d) It remains insoluble.
Question.4. Identify the compound, Z.
(a) CO_{2}
(b) H_{2}CO_{3}
(c) NaOH
(d) H_{2}O
Question.5. Sodium carbonate is a basic compound because it is a salt of a
(a) strong acid and strong base
(b) weak acid and weak base
(c) strong acid and weak base
(d) weak acid and strong base.
Ans.1. (a)
The compound of sodium that is a constituent of baking powder and is used in antacids, is sodium hydrogen carbonate ( NaHCO_{3} ).
Ans.2. (b) 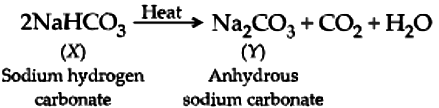
Ans.4. (b)
Z is carbonic acid, a weak acid formed when Na_{2}CO_{3} is dissolved in water.
Ans.5. (d)
Case Study Question 08
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
Sodium chloride obtained from sea water or from lakes contains many impurities such as sulphates of sodium and magnesium along with chlorides of calcium and magnesium. The chlorides of calcium and magnesium are particularly undesirable on account of their deliquescent nature.
For its purification, common salt is dissolved in minimum quantity of water to get a saturated solution from which insoluble impurities are filtered off. Then hydrogen chloride gas is passed through the saturated solution and the crystals of pure NaCl separate out. The soluble impurities remain in the mother liquor. The crystals are filtered, washed and dried.
Question.1. Select the correct statement regarding salt NaCl .
(a) Pure NaCl is hygroscopic in nature.
(b) It is soluble in alcohol.
(c) Pure NaCl is not hygroscopic, it shows hygroscopic nature due to impurities.
(d) It is a brown crystalline solid.
Question.2. Nature of aqueous solution of common salt is
(a) acidic
(b) alkaline
(c) basic
(d) neutral.
Question.3. In the given series of reactions, Y and Z respectively are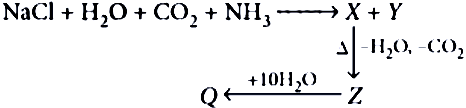
(a) NaHCO_{3} , NaOCl_{2}
(b) NH_{4}Cl , Na_{2}CO_{3}
(c) Na_{2}CO_{3} , NH_{4}Cl
(d) Na_{2}CO_{3} , NaHCO_{3}
Question.4. Which of the following compounds is alkaline in aqueous medium?
(a) Na_{2}CO_{3}
(b) NaCl
(c) H_{2}CO_{3}
(d) CuSO_{4}
Question.5. Some statements regarding salt NaCl are given below:
I. It is prepared by chlor-alkali process.
II. It is a white crystalline substance.
III. It also exists in the form of rocks and is called rock salt.
IV. It is a neutral salt, pH value of NaCl is 7.
Select the correct statements.
(a) II and III only
(b) III and IV only
(c) I and IV only
(d) II, III and IV only
Ans.1. (c)
NaCl is insoluble in alcohol and it is a white crystalline solid. Pure NaCl is not hygroscopic in nature.
Ans.2. (d)
Aqueous solution of common salt is neutral in nature. Ans.3. (b)
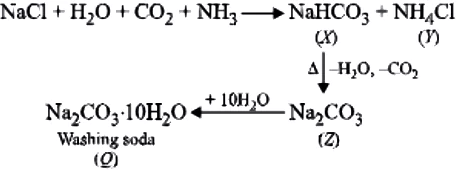
When Na_{2}CO_{3} (sodium carbonate) is dissolved in water then it forms alkaline aqueous solution due to the formation of NaOH which is a strong alkali.
Ans.5. (d)
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is prepared by chlor-alkali process.
Case Study Question 09
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
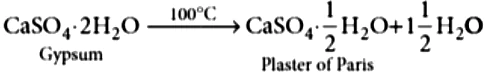
Chemically, Plaster of Paris (POP) is calcium sulphate hemihydrate, i.e., containing half molecule of water of crystallisation. It is represented by the formula, CaSO_{4}\cdot \frac{1}{2}H_{2}O . Half molecule of water of crystallisation means that one water molecule is shared by two formula units of CaSO_{4} .
Hence, we also represent its formula as \left(CaSO_{4}\right)_{2}\cdot H_{2}O . The name, plaster of Paris, was given to this compound because for the first time, it was made from gypsum which was mainly found in Paris.
Question.1. The difference of water molecules in gypsum and plaster of Paris is
(a) \frac{5}{2}
(b) 2
(c) \frac{1}{2}
(d) \frac{3}{2}
Question.2. Plaster of Paris hardens by
(a) giving off CO_{2}
(b) changing into CaCO_{3}
(c) combining with water
(d) giving out water.
Question.3. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) Plaster of Paris is used to ornate designs on walls and ceilings.
(b) On heating gypsum above 373 K, CaSO_{4} is obtained.
(c) Dead burnt plaster is CaSO_{4}\cdot 2H_{2}O .
(d) Setting of plaster is due to its hydration into gypsum.
Question.4. Select the incorrect statement with respect to gypsum.
(a) It is slightly soluble in water.
(b) It is also known as alabaster.
(c) On heating gypsum at 373 K, it loses water molecules and becomes calcium sulphate hemihydrate.
(d) Chemical formula of gypsum is CaSO_{4}\cdot \frac{1}{2}H_{2}O .
Question.5. Plaster of Paris is obtained by
(a) adding water to calcium sulphate
(b) adding sulphuric acid to calcium hydroxide
(c) heating gypsum to a very high temperature
(d) cheating gypsum to 100° C.
Ans.1. (d)
Gypsum is CaSO_{4} \cdot 2H_{2}O and plaster of Paris is CaSO_{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2} H_{2}O . Difference in number of water molecules = \frac{3}{2}
Ans.2. (c)
Plaster of Paris is hardened by combining with water.
Ans.3. (c)
Dead burnt plaster is CaSO_{4} (anhydrous calcium sulphate).
Ans.4. (d)
Gypsum: CaSO_{4} \cdot 2H_{2}O
Plaster of paris: CaSO_{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2} H_{2}O
Ans.5. (d)
Gypsum on heating upto 100°C gives plaster of Paris.
Case Study Question 10
Read the following and answer any four questions from 1 to 5.
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil : Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H^{+} and OH . The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids: A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare: Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
Question.1. When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl , its colour changes to
(a) white
(b) dark red
(c) bluish green
(d) no change.
Question.2. P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then
(a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation.
(b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralisation.
(c) pH of both P and Q decrease.
(d) pH of both P and Q increase.
Question.3. Which of the following acids is present in bee sting?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
Question.4. Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because
(a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid
(b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid
(c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid
(d) none of these.
Question.5. The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH?
(a) X only
(b) Y only
(c) Both X and Y
(d) None of these
Ans.1. (c) Ans.2. (a)
On diluting, H^{+} ion concentration reduces per unit volume thus, pH increases.
On the other hand, on diluting, OH^{-} concentration also reduces, pOH increases and pH decreases. As, pOH + pH = 14.
Thus, pH of Q (basic solution) decreases while that of P (acidic solution) increases on dilution.
Ans.3. (c)
Formic acid is the common name of methanoic acid, and it is present in bee sting.
Ans.4. (c)
Ans.5. (b)
Soil Y is acidic. Hence, it should be treated with powdered chalk to reduce its acidity.