Hint: List down the reasons for changes in DNA copying and their effect on ecosystem, in order to understand importance of variations.
Question.1. The image shows the model of a family of dogs. 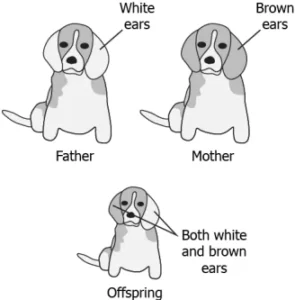
(a) variation in the genetic material
(b) fast multiplication of body cells
(c) asexual mode of reproduction
(d) effect of environment on the offspring
Question.2. A population of thermophilic archaebacteria are generally found in hot springs. Any change to the temperature of the water affects the survival of the archaeabacteria. If the temperature of hot springs gets reduced, change in which component can allow survival of few members of these archaeabacteria?
(a) cell wall
(b) cytoplasm
(c) DNA
(d) ribosomes
Ans.1. (a) variation in the genetic material
Ans.2. (c) DNA
Hint: Illustrate the process of fission in amoeba, leishmania & plasmodium, in order to understand how uni-cellular organisms divide.
Question.3. The image shows the process of division in plasmodium.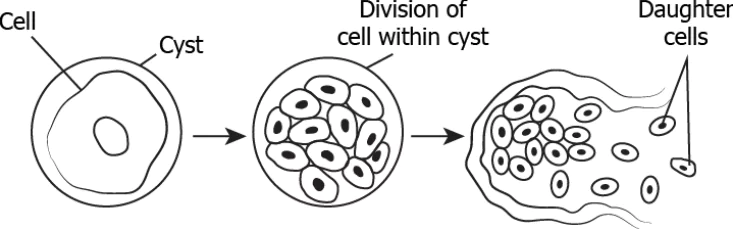
(a) The cyst divides repeatedly to form many daughter cells.
(b) The cell divides multiple times giving rise to many daughter cells.
(c) The nucleus divides repeatedly inside the cell to form new daughter cells.
(d) The cyst enlarges in size and then bursts producing many new daughter cells.
Question.4. The image shows the process of binary fission in amoeba.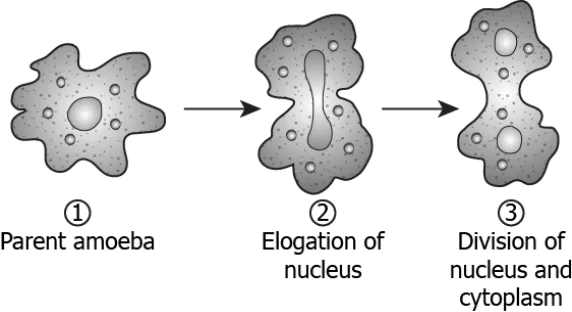
(a) Parent cell will lead to the formation of four daughter cells of equal sizes.
(b) Parent cell will lead to the formation of two daughter cells of equal sizes.
(c) Parent cell will lead to the formation of four daughter cells of different sizes.
(d) Parent cell will lead to the formation of two daughter cells of different sizes.
Ans.3. (b) The cell divides multiple times giving rise to many daughter cells.
Ans.4. (b) Parent cell will lead to the formation of two daughter cells of equal sizes.
Hint: Illustrate the process of fragmentation in Spirogyra & spore formation in Rhizopus, in order to understand how multi-cellular organisms with simple body design divide.
Question.5. The image shows the formation of spores in Rhizopus.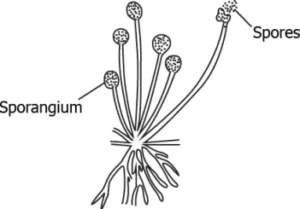
(a) spores divide and grow into new individual
(b) spores combine with other spores and grow
(c) spores enlarge in size for the growth of new individual
(d) spores land on other organisms and increase with their growth in size
Question.6. The image shows the division in Spirogyra.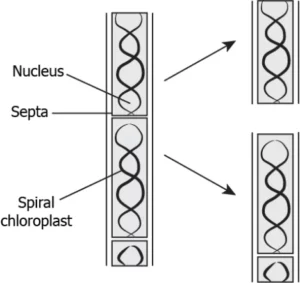
(a) It is a multicellular organism gives rise to two new equal sized individuals.
(b) It is a unicellular organism that gives rise to two new equal sized individuals.
(c) It is a unicellular organism that breaks into pieces that grows into new individuals.
(d) It is a multicellular organism that breaks into pieces that grows into new individuals.
Ans.5. (a) spores divide and grow into new individual
Ans.6. (d) It is a multicellular organism that breaks into pieces that grows into new individuals.
Hint: Illustrate the process of regeneration in Planaria, in order to understand how fully differentiated multi-cellular organisms divide.
Question.7. A student takes a planaria in the lab and cuts into three parts as shown.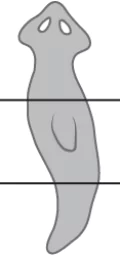
(a) the cells around the cut start to divide to form lost part
(b) the cells around the cut enlarge to take the shape of lost part
(c) the cells around the cut start to divide to form a complete organism
(d) the cells around the cut attracts other planarians to fuse with the separated part
Question.8. A student observes the process of regeneration in Planaria.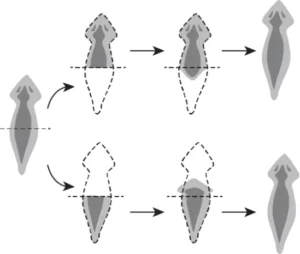
(a) It is a single celled organism.
(b) All planarians share the same genome.
(c) Division in Planaria involves a single parent.
(d) Planaria divides only under unfavourable condition.
Ans.7. (c) the cells around the cut start to divide to form a complete organism
Ans.8. (c) Division in Planaria involves a single parent.
Hint: Illustrate the process of budding in Hydra, in order to understand how fully differentiated multi-cellular organisms use regenerative cells to divide.
Question.9. The image shows a bud developing on a Hydra.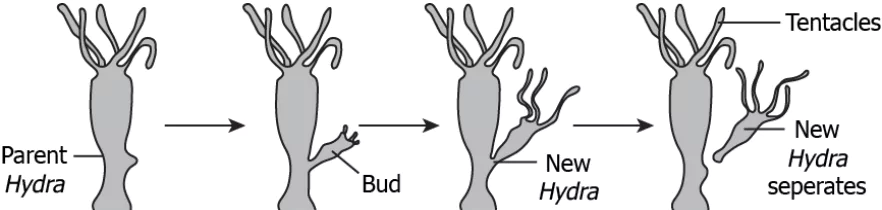
(a) bud develops due to separation of body parts of Hydra
(b) bud develops due to repetitive cell division at a specific site
(c) bud develops due to change in the environmental conditions
(d) develops due to attachment of another Hydra at a specific site
Question.10. The model shows the process of budding in Hydra.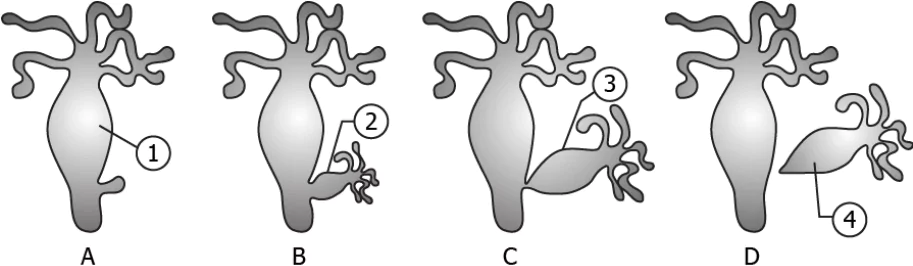
(a) to increase the body size
(b) to recover lost body parts
(c) to induce variation in body
(d) to develop new independent individual
Ans.9. (b) bud develops due to repetitive cell division at a specific site
Ans.10. (d) to develop new independent individual
Hint: Illustrate the process of vegetative propagation in plants like sugarcane, roses, grapes in order to understand how plants reproduce without seeds.
Question.11. The image shows the process of vegetative propagation in a plant. 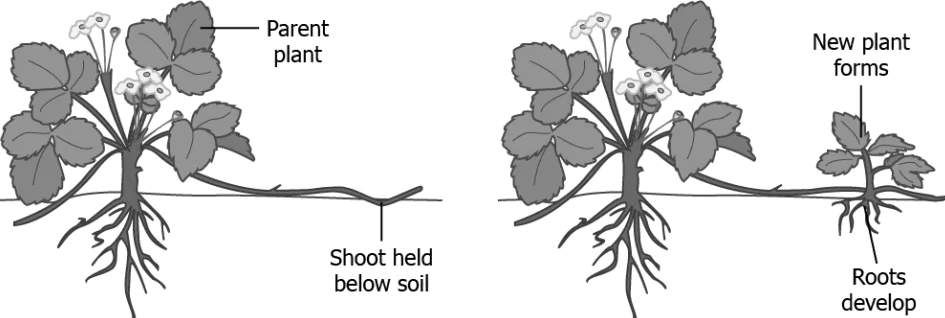
(a) this results in plant of different flowers
(b) this helps grow plants without adding extra manure
(c) this eliminates the need of producing plant using seeds
(d) this allows growth of plants with new genetic composition
Question.12. The image shows the production of a new sugarcane from an existing sugarcane plant.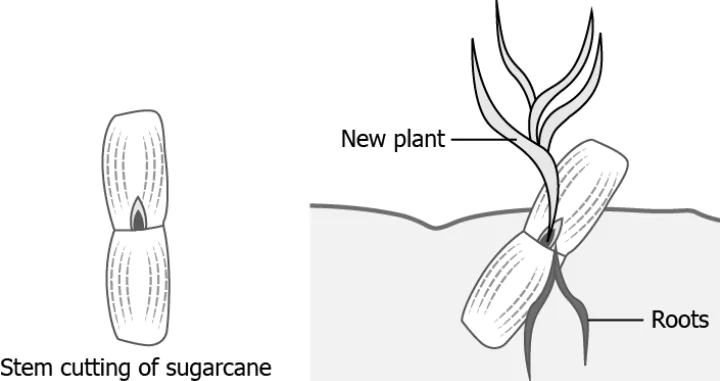
(a) It is a sexual method of producing new plants.
(b) It is an asexual method of producing new plants.
(c) It does not require a parent plant for reproduction.
(d) It involves fusion two parts of a single parent for reproduction.
Ans.11. (c) this eliminates the need of producing plant using seeds
Ans.12. (b) It is an asexual method of producing new plants.
Hint: Label the different parts of a flower and explain their functions, in order to understand how flowers reproduce to form fruit.
Question.13. The image shows the different parts of a flower. 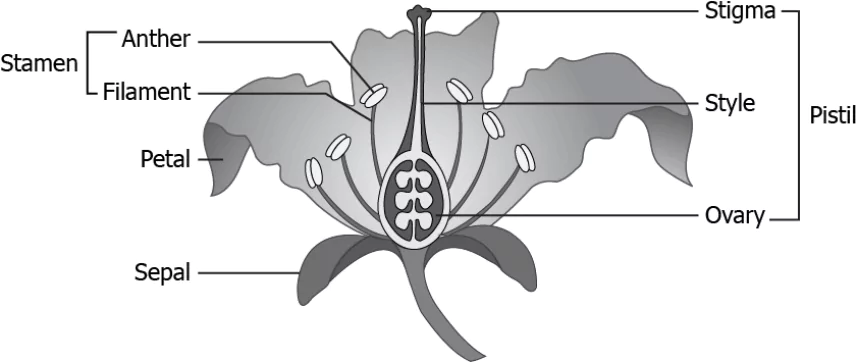
(a) anther
(b) ovary
(c) petal
(d) stigma
Question.14. The image shows the structure of a flower. 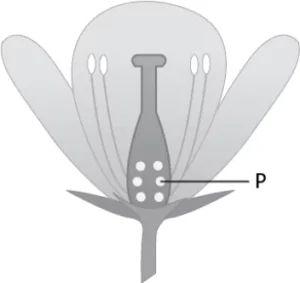
(a) formation of fruit
(b) transport of pollen
(c) formation of pollen
(d) development of pollen tube
Ans.13. (d) stigma
Ans.14. (a) formation of fruit
Hint: List down the changes occurring in male and female body in teenage years, in order to understand effects of puberty.
Question.15. Which option correctly lists the changes that occur in males during puberty?
(a) 


Question.16. The table shows the changes that occur in girls during puberty.
(a) aging of the body
(b) sexual maturation
(c) production of germ cells
(d) abnormal division of the cells
Ans.15. (a) 
Hint: Illustrate the male reproductive system, in order to understand its function in reproduction.
Question.17. The image shows the male reproductive system.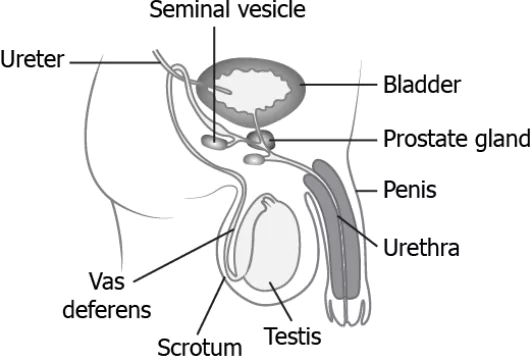
(a) testis → ureter → urethra → penis
(b) testis → vas deferens → ureter → penis
(c) testis → ureter → vas deferens → penis
(d) testis → vas deferens → urethra → penis
Question.18. The image shows the male reproductive system outside abdominal cavity.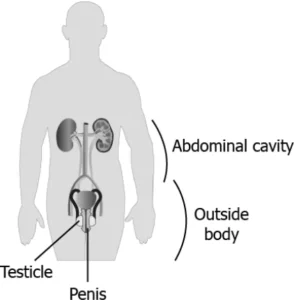
(a) delayed puberty
(b) sperm formation
(c) increase in body temperature
(d) change in genetic composition of sperms
Ans.17. (d) testis → vas deferens → urethra → penis
Ans.18. (a) delayed puberty
Hint: Illustrate the female reproductive system, in order to understand its function in reproduction.
Question.19. The image shows the reproductive organ in females.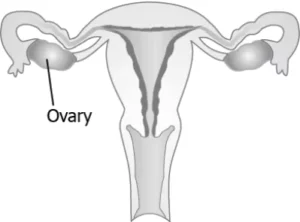
(a) fertilisation
(b) synthesis of eggs
(c) production of eggs
(d) growth and development of embryo
Question.20. The image shows the female reproductive system.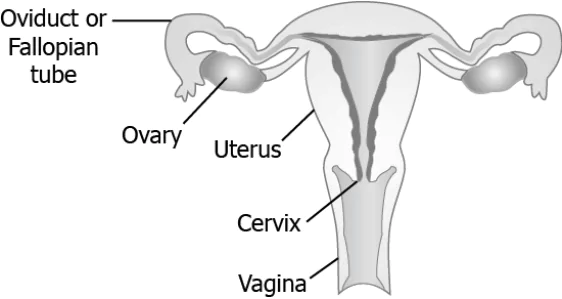
(a) release of eggs
(b) entering of sperms
(c) maturation of eggs
(d) implantation of embryo
Ans.19. (c) production of eggs
Ans.20. (d) implantation of embryo
Hint: Describe the changes taking place in female body after/ without fertilization, in order to understand human reproduction.
Question.21. The table lists some changes that occur inside the female body after fertilization of egg with sperm. 
(a) C → B → E → A → D
(b) E → C → D → B → A
(c) E → C → B → D → A
(d) C → E → A → B → D
Question.22. After a female attains puberty, the body undergoes many changes for maturation. Which event will likely happen in the female body when there is no fertilization of egg?
(a) disintegration of uterine wall
(b) development of egg into zygote
(c) increase in the production of eggs in the ovaries
(d) of a mature egg into an immature egg
Ans.21. (c) E → C → B → D → A
Ans.22. (a) disintegration of uterine wall
Hint: List down the ways to avoid fertilization, in order to avoid pregnancy and maintain reproductive health.
Question.23. Which contraceptive can be used to prevent the entry of sperm inside the female reproductive organ?
(a) inserting copper-T inside the uterus
(b) wearing condoms on the penis
(c) consuming oral pills containing hormones
(d) undergoing surgery for blocking fallopian tube
Question.24. The image shows a surgical method in females to prevent pregnancy.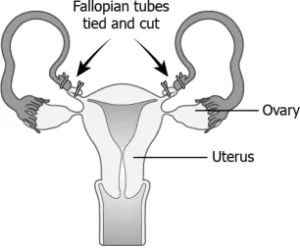
(a) maturation of eggs
(b) production of eggs
(c) entry of eggs into the uterus
(d) entry of sperm into the uterus
Ans.23. (b) wearing condoms on the penis
Ans.24. (c) entry of eggs into the uterus




