Hint: Identify properties of given items and select a property that would help them
easily separate the items from each other.
Question.1. The image shows the process of winnowing.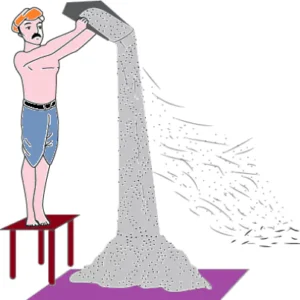
(a) Size
(b) Shape
(c) Colour
(d) Weight
Question.2. The image shows the two types of marbles in the jar.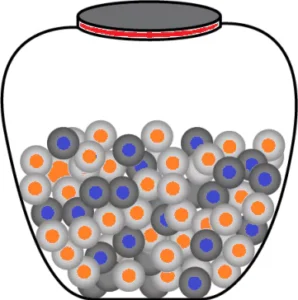
(a) On the basis of size
(b) On the basis of colour
(c) On the basis of shape
(d) On the basis of weight
Ans.1. (d) Weight
Ans.2. (b) On the basis of colour
Hint: Outlines methods that can be adapted in everyday life situations such as separation of husk from grains, grain from stalks, separation of fine sand from coarse sand.
Question.3. A sample of flour has ungrounded wheat grains mixed in it. Which method can be used to separate the wheat grains from the flour?
(a) Sieving
(b) Filtration
(c) Threshing
(d) Sedimentation
Question.4. While making the tea, which method of separation is used to separate the tea leaves?
(a) Filtration
(b) Evaporation
(c) Decantation
(d) Sedimentation
Ans.3. (a) Sieving
Ans.4. (a) Filtration
Hint: Carries out some of the improvised procedures of separation of insoluble solids from liquids in a given situation.
Question.5. A student has a solution of sand and water. What method can be used to separate sand from the water easily?
(a) Mix a chemical in the solution
(b) Place the solution in the sunlight
(c) Stir the solution and leave the beaker undisturbed
(d) Pour the solution into another beaker using a sieve
Question.6. The table shows the materials required for a filtration process.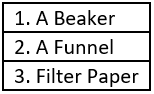
(a) 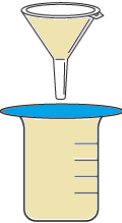
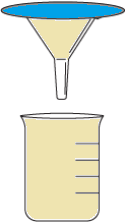
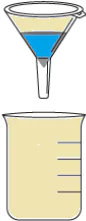
Ans.5. (d) Pour the solution into another beaker using a sieve
Ans.6. (c)
Hint: Explains how multiple processes can be employed when the mixture has a soluble and insoluble component.
Question.7. A student has a solution of salt, sand and water. Which option explains the processes required to separate the salt and sand from water?
(a) Evaporation to remove sand, filtration to obtain salt
(b) Filtration to remove sand, evaporation to obtain salt
(c) Filtration to remove sand, sedimentation to obtain salt
(d) Sedimentation to remove sand, filtration to obtain salt
Question.8. A student has a sample of raw rice in a container. The student added water in the container to wash it. After some time, the dust particles come at the surface while the rice grains settle down at the bottom. Which processes would help remove the dust particles?
(a) Filtration and evaporation
(b) Condensation and evaporation
(c) Evaporation and sedimentation
(d) Decantation and sedimentation
Ans.7. (b) Filtration to remove sand, evaporation to obtain salt
Ans.8. (d) Decantation and sedimentation
Hint: Arrives at logical conclusion that certain specific methods can be employed to separate different substances present in a mixture based on the size, colour, weight or solubility of the components.
Question.9. A bag has the limes and oranges. A student separates them by the method of handpicking without looking inside the bag directly. Why do you think the student uses the method of handpicking in this case?
(a) Because both fruits have different size
(b) Because both fruits have different colour
(c) Because both fruits have different shape
(d) Because both the fruits have different weight
Question.10. A student heated a salt water solution to obtain the salt from the solution. Why the student heated the salt water solution?
(a) Because salt evaporates easily
(b) Because salt is soluble in water
(c) Because salt is lighter and comes at the surface
(d) Because salt settles at bottom in water
Ans.9. (a) Because both fruits have different size
Ans.10. (b) Because salt is soluble in water
Hint: Examine the solubility of salt in water in certain conditions in order differentiate the solution as saturated and unsaturated.
Question.11. A student takes some cold water in a beaker and dissolves two tablespoons of salt in it. When the student adds one more tablespoon of salt it gets settled at the bottom of the beaker. The student warms the water and observes that the salt disappears. What can be the reason for this observation?
(a) Heat increases the solubility of water
(b) Heat evaporates the excess salt in solution
(c) After heating the solution become saturated
(d) Two table spoon of salt makes the solution unsaturated
Question.12. A salt solution gets saturated when a student mixes 5 g of salt in 30 ml of water in a beaker. The student further added 5 g of salt in the solution that does not dissolve in water. The student adds 20 ml of water in the beaker and observes some of the salt is dissolved.
How much water is needed to dissolve the remaining salt?
(a) 5 ml
(b) 10 ml
(c) 20 ml
(d) 30 ml
Ans.11. (a) Heat increases the solubility of water
Ans.12. (b) 10 ml