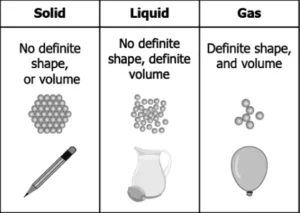
Hint: Classify matter into solids, liquids and gases based on characteristic properties of the particles in them.
Question.1. A student notices that a substance “X” has fixed volume and can be transferred from one container to another. Which option correctly classifies the substance “X”?
(a) 


Question.2. The image given below shows data about the different types of matter.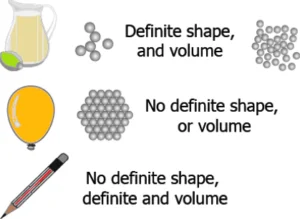
(a) 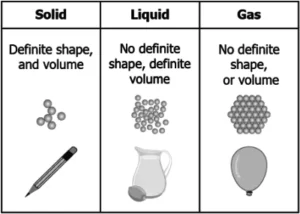
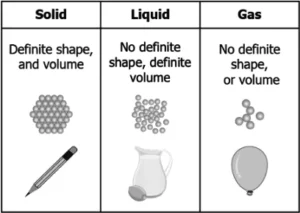
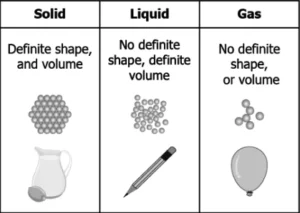
Ans.1. (d) 
Hint: Demonstrate that matter is made up of tiny particles.
Question.3. A student adds 5 g sugar in 100 mL water. The student stirs the contents for 2 minutes.
After some time, the student notices a clear solution. Why the student was unable to see sugar particles?
(a) they are colorless
(b) they settle at the bottom
(c) they are too small to be seen
(d) they evaporate when added to water
Question.4. A student pours 20 mL flavored water in a glass containing plain water and notices that the taste of the water changes. The students repeat the activity for 10 times and reports that the water still has some flavor. What can be the possible reason for this?
(a) The flavor from the water can never be removed by any method.
(b) The water is made flavored in such a way that it remains the same until it is consumed.
(c) Sieves were not used in the experiment which would have helped to remove flavored particles from the water.
(d) The particles of flavored water are very small and are transferred to plain water even when added in very small quantities.
Ans.3. (c) they are too small to be seen
Ans.4. (d) The particles of flavored water are very small and are transferred to plain water even when added in very small quantities.
Hint: Infer that intermolecular space between particles of solids makes diffusion possible between matter.
Question.5. A student adds ink to water. The ink particles spread throughout the water. Which property of water allows other particles to diffuse in it?
(a) fixed volume
(b) inability to compress
(c) intermolecular spaces
(d) ability to change shape
Question.6. A student put an equal amount of potassium permanganate powder over a glass plate and in a beaker filled with water. The student rubbed the surface of the plate and stir the contents of the beaker. It was observed that the permanganate powder dissolved in the water and formed a colored solution. Which option explains the reason for the student’s observation?
(a) Water is a liquid and can dissolve and solid particles in it.
(b) The ability of water to exist in any state allows it to dissolve any substance
(c) Water has large intermolecular spaces which allow molecules of other substances to get between those spaces
(d) Water particles are tightly arranged in an orderly fashion which allows the binding of the molecules of other substances
Ans.5. (c) intermolecular spaces
Ans.6. (c) Water has large intermolecular spaces which allow molecules of other substances to get between those spaces
Hint: Conclude that particles of matter continuously move during interaction between various forms and change in temperature changes the kinetic energy of particles.
Question.7. A student learns that the speed of the formation of a solution increases when the heat is supplied. How does heat affect the formation of the solution?
(a) change in temperature increases the size of the water particles
(b) change in temperature changes the shape of the water particles
(c) change in temperature changes the kinetic energy of the particles
(d) change in temperature decreases the inter-molecular spaces between the particles
Question.8. A student puts one drop of food colour in 100 mL of water. The student notices that the food colour gradually spreads in the water. What is the possible reason for this phenomenon?
(a) a close arrangement of the water particles
(b) the ability of the water particles to move continuously
(c) the ability of the water to stay warm at room temperature
(d) small intermolecular space between the water particles
Ans.7. (c) change in temperature changes the kinetic energy of the particles
Ans.8. (d) small intermolecular space between the water particles
Hint: Conclude that particles of mater attract each other and depict the molecular arrangement of particles in the three states of matter, i.e., solids, liquids and gases.
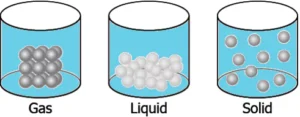
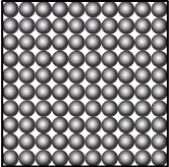
Question.9. A student learns that the particles of brick are arranged in a manner so that they attract each other with greater force. Which diagram shows the arrangement of particles in a brick?
(a) 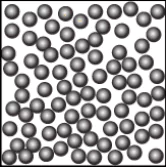
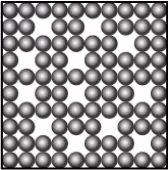
Question.10. A student has a glass of hot water which is covered with a plate. The student wants to transfer the hot water into another glass. The student notices that as he lifts the plate, some air flows upwards as he carefully pours water. The student makes particle diagrams of steam, water and gas. Which diagram correctly shows the particle arrangement?
(a) 
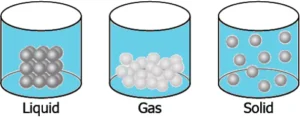
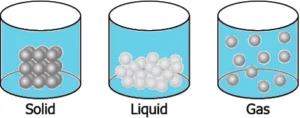
Ans.9. (b) 
Hint: Describe the physical properties of solids and illustrate their molecular
arrangements.
Question.11. What is the property of a solid substance?
(a) It retains its shape.
(b) It changes its volume.
(c) It retains its colour.
(d) It changes its mass.
Question.12. A student made a model to show how particles of a substance X are arranged. 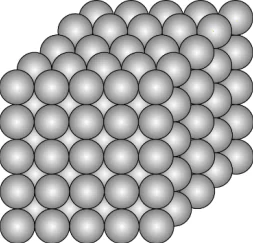
(a) The particles are closely packed that allows Substance X to change its volume.
(b) The particles are fixed at their positions that allows Substance X to retain its shape.
(c) The particles are bonded to each other that allows Substance X to maintain a fixed mass.
(d) The particles are identical to each other that allows Substance X to have a uniform composition.
Ans.11. (a) It retains its shape.
Ans.12. (b) The particles are fixed at their positions that allows Substance X to retain its shape.
Hint: Identify the distinguishing characteristics of liquids.
Question.13. A liquid substance retains its
(a) volume but not its shape.
(b) shape but not its volume.
(c) volume but not its mass.
(d) mass but not its volume.
Question.14. Mohit has a bowl filled with a Substance P. He notes some of his observations. 
(a) A gas because it has a volume.
(b) A solid because it has a fixed mass.
(c) A liquid because its shape changes.
(d) A gas because objects can pass through it.
Ans.13. (a) volume but not its shape.
Ans.14. (c) A liquid because its shape changes.
Hint: Identify the characteristic features of gases and compare the three states of matter.
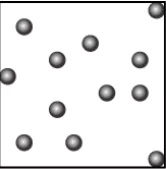
Question.15. A student wants to make a model to show how particles of a gas are arranged. He uses red marbles, where each marble represents one gas particle. Which model should the student make?
(a) 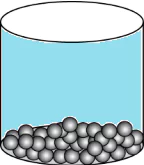
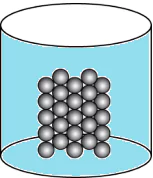
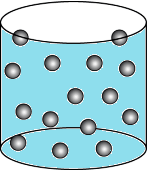
Question.16. The table shows three substances and their properties.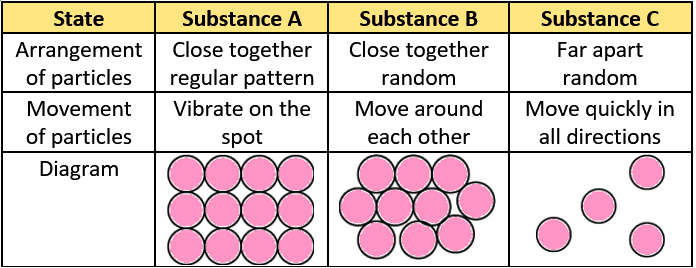
(a) Substance A only
(b) Substance C only
(c) Substance A and B
(d) Substance B and C
Ans.15. (c) 
Hint: Provide scientific explanation for diffusion in examples of gases and liquids
witnessed in real life.
Question.17. Meenal lights an incense stick in her room. A moment later the fragrance of the stick spreads throughout the house. What explains the phenomenon?
(a) Gas particles carry a specific odour.
(b) Gas particles are found everywhere in air.
(c) Gas particles move fast and spread everywhere.
(d) Gas particles are closely spaced and vibrate fast.
Question.18. A student did an activity where he put a drop of ink in water. He noticed that as soon as the drop falls in water, the blue ink spreads throughout.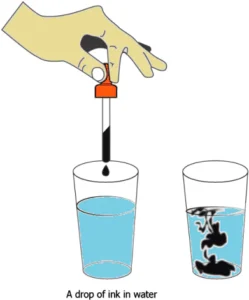
(a) because liquids have a fixed volume
(b) because liquids do not have a fixed shape
(c) because the particles of liquids can move around
(d) because the particles of liquids are closely spaced
Ans.17. (c) Gas particles move fast and spread everywhere.
Ans.18. (c) because the particles of liquids can move around
Hint: Explain the effect of change in temperature on states of matter.
Question.19. Why does an ice cube melt when put out of the refrigerator?
(a) because it loses heat and its particles move faster and farther causing melting
(b) because it loses heat and its particles gain kinetic energy changing from solid to liquid
(c) because it gains heat and its particles come closer since the force of attraction increases
(d) because it gains heat and its particles start moving faster and overcome the force of attraction
Question.20. What happens when the temperature of ice is increased above 0°C?
(a) The molecules gain kinetic energy and ice changes into water
(b) The molecules lose kinetic energy and ice changes into water
(c) The molecules gain kinetic energy and ice changes into vapour
(d) The molecules lose kinetic energy and ice changes into vapour
Ans.19. (d) because it gains heat and its particles start moving faster and overcome the force of attraction
Ans.20. (a) The molecules gain kinetic energy and ice changes into water
Hint: Relate the effect of pressure on different states of matter and its applications.
Question.21. Cooking gas is known as LPG (Liquified Petroleum Gas). How can a gas be liquified?
(a) when pressure is applied to the gas
(b) when temperature of the gas is increased
(c) when gas is mixed with a liquid substitute
(d) when the force of attraction between particle is reduced
Question.22. Gases are easily compressible by applying pressure. The same volume of gas can fill up a small can and can spread into a big room. What is the relationship between the property of gases and compressibility?
(a) Gas particles have large spaces between them, so when pressure is applied, the particles compress.
(b) Gas particles have strong intermolecular forces, so when pressure is applied, the particles liquify.
(c) Gas particles have high kinetic energy, so when pressure is applied, the particles lose their energy.
(d) Gas particles have more speed, so when pressure is applied, the particles move farther away and compress.
Ans.21. (a) when pressure is applied to the gas
Ans.22. (a) Gas particles have large spaces between them, so when pressure is applied, the particles compress.
Hint: Identify the various processes during change of substances from one physical
state to another and classify substances on this basis.
Question.23. The image shows two changes.
(a) Process X – freezing; Process Y – melting
(b) Process X – melting; Process Y – evaporation
(c) Process X – condensation; Process Y – melting
(d) Process X – evaporation; Process Y – condensation
Question.24. The image shows three substances that can change from one physical state to another by different processes.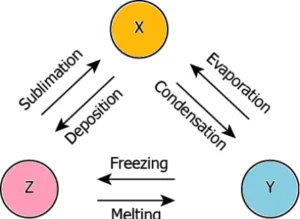
(a) X – gas, Y – liquid, Z – solid
(b) X – liquid, Y – solid, Z – gas
(c) X – gas, Y – solid, Z – liquid
(d) X – solid, Y – gas, Z – liquid
Ans.23. (b) Process X – melting; Process Y – evaporation
Ans.24. (a) X – gas, Y – liquid, Z – solid
Hint: Postulate the reason for constancy of temperature during the change in states
of matter.
Question.25. The melting point of ice is 0°C. At this temperature, both ice and water exist. However, the particles of water at 0°C have more energy than particles of ice at 0°C. What explains this?
(a) at melting point, water particles absorb more heat and change into ice
(b) at melting point, ice particles raise their temperature and change to water
(c) at melting point, water particles raise their temperature and change into ice
(d) at melting point, ice particles absorb latent heat and change into water particles
Question.26. When ice is given heat, it reaches a temperature of 0°C and starts melting. The more heat is gained, the more it changes to water. However, the temperature remains constant at 0°C until all ice changes to water. Why does the temperature remain constant?
(a) because of the latent heat of fusion
(b) because of the kinetic energy of ice particles
(c) because of the latent heat of vaporization
(d) because of the kinetic energy of water particles
Ans.25. (d) at melting point, ice particles absorb latent heat and change into water particles
Ans.26. (a) because of the latent heat of fusion
Hint: Explain situations that demonstrate factors affecting evaporation.
Question.27. Clothes do not dry quickly when there is more humidity in air. What explains the phenomenon?
(a) high humidity decreases the rate of evaporation
(b) high humidity increases the rate of evaporation
(c) high humidity decreases the rate of condensation
(d) high humidity increases the rate of condensation
Question.28. A student has four containers of different shapes and sizes but made of steel.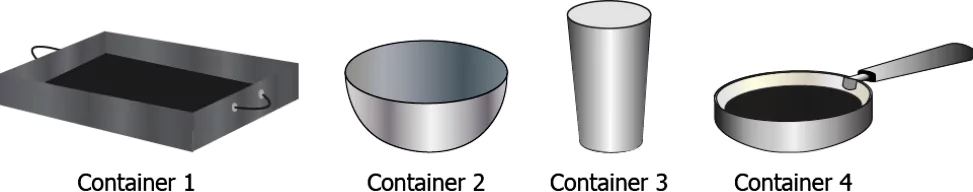
(a) container 1
(b) container 2
(c) container 3
(d) container 4
Ans.27. (a) high humidity decreases the rate of evaporation
Ans.28. (a) container 1
Hint: Provide explanation for life situations that demonstrate effects of evaporation.
Question.29. Kabir came back home after playing football. He felt hot and sweaty. He stood under the fan. He noticed he started feeling cool and dry. What explains his observation?
(a) When sweat evaporates, warm air moves away from the body.
(b) When sweat evaporates, it gains heat energy from the surroundings.
(c) When sweat evaporates, it absorbs energy from the body making it cooler.
(d) When sweat evaporates, cooler air from the surroundings reaches the body.
Question.30. During summers people sprinkle water on the rooftops because
(a) water keeps heat away from the house.
(b) when water evaporates, it absorbs the heat from the rooftops.
(c) when water condenses on the rooftops, the house remains cool.
(d) water absorbs cold from the surroundings and keeps the house cool.
Ans.29. (c) When sweat evaporates, it absorbs energy from the body making it cooler.
Ans.30. (b) when water evaporates, it absorbs the heat from the rooftops.