Revision Notes for Class 10 IT (402) – Chapter 1 Communication Skills II
Are you confused on Revision Notes? Revision Notes for class 10 IT (402) – Chapter 1 Communication Skills II is the right place to refer. Communication Skills revision notes are designed in such a way that students can directly read them without any difficulty. Lets get started…
Revision Notes of Communication Skills
- It is a process which involves sharing of information, opinion, ideas, and beliefs between two or more persons through a continuous activity of speaking, listening and understanding.
- The word ‘communication’ comes from the Latin word commūnicāre, meaning ‘to share’.
Parts of Communication
Communication has three important parts:
- Transmitting — The sender transmits the message through one medium or another.
- Listening — The receiver listens or understands the message.
- Feedback — The receiver conveys their understanding of the message to the sender in the form of feedback to complete the communication cycle.
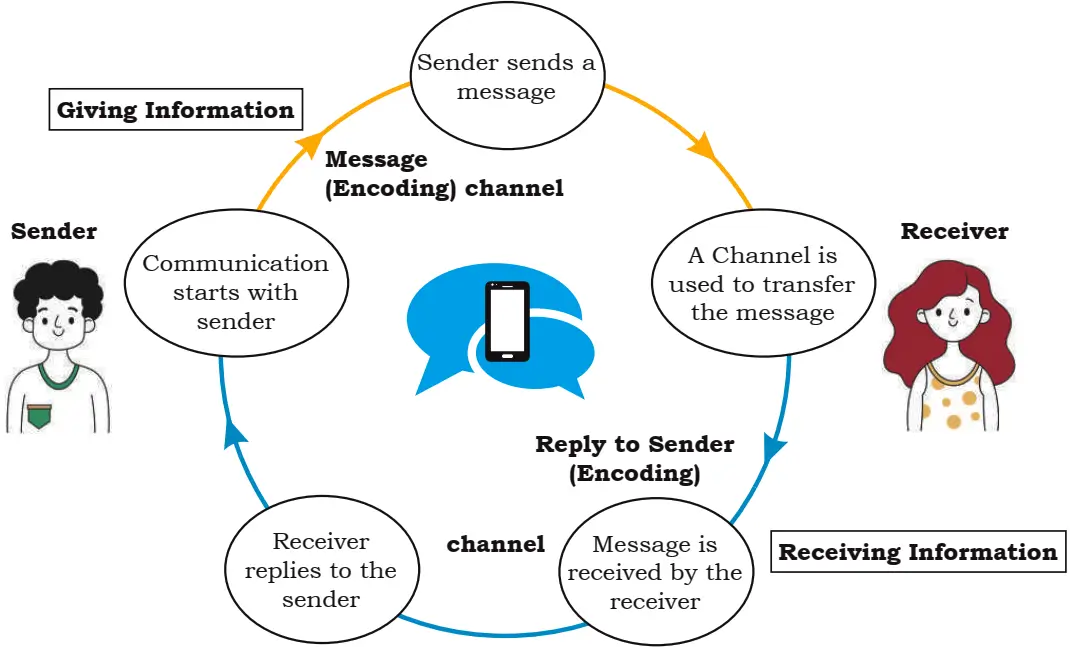
Elements of a Communication
The various elements of a communication cycle are:
- Sender: the person beginning the communication.
- Message: the information that the sender wants to convey.
- Channel: the means by which the information is sent.
- Receiver: the person to whom the message is sent.
- Feedback: the receiver’s acknowledgement and response to the message.
Methods of Communication
1. Face-to-face informal Communication
Description:
- There is nothing better than face-to-face communication.
- It helps the message to be understood clearly and quickly.
- Also, since body language can be seen in this case; it adds to the effectiveness of the communication.
2. E-mail
Description:
- E-mail can be used to communicate quickly with one or many individuals in various locations.
- It offers flexibility, convenience and lowcost.
3. Notices/Posters
Description:
- It is effective when the same message has to go out to a large group of people.
- Generally used for where email communication may not be effective.
- For example, ‘Change in the lunch time for factory worker,’ or ‘XYZ Clothing will remain closed for customers on Sunday.’
4. Business Meetings
Description:
- Communication during business meetings at an organisation are generally addressed to a group of people.
- It can be related to business, management and organisational decisions.
5. Other Methods
Description: There can be various other methods like social networks, message, phone call for communication, newsletter, blog, etc.
Verbal Communication
Verbal communication includes sounds, words, language, and speech. Speaking is one of the most effective and commonly used way of communicating. It helps in expressing our emotions in words.
Types of Verbal Communication
(I). Interpersonal Communication
Description: This form of communication takes place between two individuals and is thus a one-on-one conversation. It can be formal or informal.
Examples:
1. A manager discussing the performance with an employee.
2. Two friends discussing homework.
3. Two people talking to each other over phone or video call.
(II).Written Communication
Description: This form of communication involves writing words. It can be letters, circulars, reports, manuals, SMS, social media chats, etc. It can be between two or more people.
Examples:
1. A manager writing an appreciation e-mail to an employee.
2. Writing a letter to grandmother enquiring about health.
(III). Small Group Communication
Description: This type of communication takes place when there are more than two people involved. Each participant can interact and converse with the rest.
Examples:
1. Press conferences
2. Board meetings
3. Team meetings
(IV). Public Communication
Description: This type of communication takes place when one individual addresses a large gathering.
Examples:
1. Election campaigns
2. Public speeches by dignitaries
Advantages of Verbal Communication
- It is an easy mode of communication in which you can exchange ideas by saying what you want and get a quick response.
- Verbal communication also enables you to keep changing your interaction as per the other person’s response.
Disadvantages of Verbal Communication
Since verbal communication depends on written or spoken words, sometimes the meanings can be confusing and difficult to understand if the right words are not used.
Non-Verbal Communication
- Non-verbal communication is the expression or exchange of information or messages without using any spoken or written word.
- In other words, we send signals and messages to others, through expressions, gestures, postures, touch, space, eye contact and para language.
Importance of Non-verbal Communication
In our day-to-day communication
- 55% communication is done using body movements, face, arms, etc.
- 38% communication is done using voice, tone, pauses, etc.
- only 7% communication is done using words.
(I) Gestures
Examples:
1. Raising a hand to greet or say goodbye
2. Pointing your finger at someone
(II) Expressions
Examples:
1. Smiling when you are happy
2. Making a sad face when you are sad
(III) Body Language
Examples: Postures by which attitudes and feelings are communicated. Standing straight, showing interest.
Types of Non-Verbal Communication
1. Facial Expressions
What it means: Our expressions can show different feelings, such as Happiness, Sadness, Anger, Surprise, Fear, etc.
How to use effectively:
- Smile when you meet someone.
- Keep your face relaxed.
- Match your expressions with your words.
- Nod while listening.
2. Posture
What it means: Postures show our confidence and feelings. For example, a straight body posture shows confidence while a slumped posture is a sign of weakness.
How to use effectively:
- Keep your shoulders straight and body relaxed.
- Sit straight while resting your hands and feet in relaxed position.
- While standing, keep your hands by your sides.
3. Gestures or Body Language
What it means: Gestures include body movements that express an idea or meaning. For example, raising a hand in class to ask a question and biting nails when nervous.
How to use effectively:
- Keep your hands open.
- Avoid pointing your finger at people.
- Tilt your head a bit to show that you are attentive.
4. Touch
What it means: We communicate a great deal through touch. For example, a firm handshake to display confidence and pat on the back to encourage someone.
How to use effectively:
- Shake hands firmly while meeting someone.
- Avoid other touch gestures during formal communication.
5. Space
What it means: Space is the physical distance between two people. The space between two persons while communicating, generally depends on the intimacy or closeness between them.
How to use effectively:
- Maintain proper space depending on the relationship, which could be formal or informal or the closeness with the person with whom you are talking.
6. Eye Contact
What it means: The way we look at someone can communicate a lot. Eye contact shows that we are paying attention to the person as opposed to looking away, which can make the other person feel ignored.
How to use effectively:
- Look directly at the person who is speaking.
- Avoid staring; keep a relaxed look.
- Maintain eye contact with intermittent breaks.
7. Paralanguage
What it means: How we speak affects our communication and includes the tone, speed and volume of our voice. For example, talking fast may show happiness, excitement or nervousness while speaking slow may show seriousness or sadness.
How to use effectively:
- Use a suitable tone and volume
- Maintain a moderate speed while talking
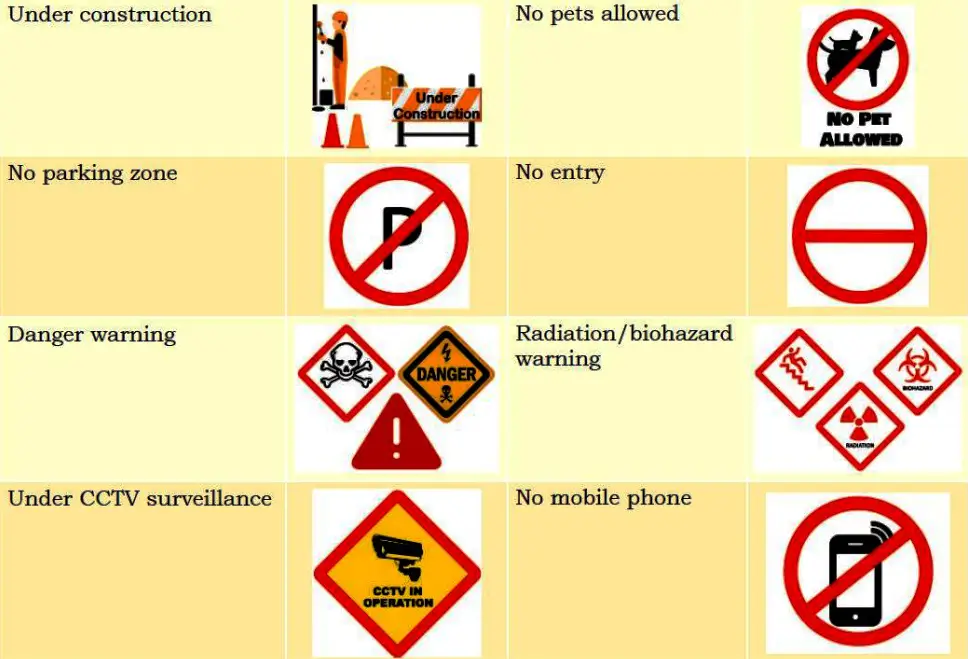
Visual Communication
Visual communication proves to be effective since it involves interchanging messages only through images or pictures and therefore, you do not need to know any particular language for understanding it. It is simple and remains consistent across different places.
Examples of Visual Communication![Examples of Visual Communication]()
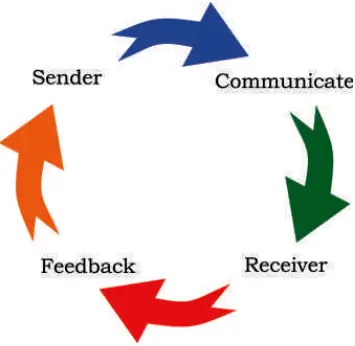
Communication Cycle and Importance of feedback
- Feedback is an important part of the communication cycle. For effective communication, it is important that the sender receives an acknowledgement from the receiver about getting the message across.
- While a sender sends information, the receiver provides feedback on the received message.
- Translated to the work environment, when you observe someone perform their work and then, communicate with them to help improve their performances, you are giving feedback.
Types of Feedback
1. Positive Feedback
Examples:
- I noticed you finished the work perfectly. Great job!
- I really appreciate you taking that call. Can you please also share the details?
2. Negative Feedback
Examples:
- You keep forgetting to smile at the hotel guests when you talk to them.
- You take really long to reply to e-mails! Are you always so busy?
3. No Feedback
Examples:
- It is also a feedback in itself which indicates disagreement of ideas.
A good feedback is one that is:
- Specific: Avoid general comments. Try to include examples to clarify your statement. Offering alternatives rather than just giving advice allows the receiver to decide what to do with your feedback.
- Timely: Being prompt is the key, since feedback loses its impact if delayed for too long.
- Polite: While it is important to share feedback, the recipient should not feel offended by the language of the feedback.
- Offering continuing support: Feedback sharing should be a continuous process. After offering feedback, let recipients know you are available for support.
Importance of feedback
Feedback is the final component and one of the most important factors in the process of communication since it is defined as the response given by the receiver to the sender. Let us look at certain reasons why feedback is important.
- It validates effective listening: The person providing the feedback knows they have been understood (or received) and that their feedback provides some value.
- It motivates: Feedback can motivate people to build better work relationships and continue the good work that is being appreciated.
- It is always there: Every time you speak to a person, we communicate feedback so it is impossible not to provide one.
- It boosts learning: Feedback is important to remain focussed on goals, plan better and develop improved products and services.
- It improves performance: Feedback can help to form better decisions to improve and increase performance.
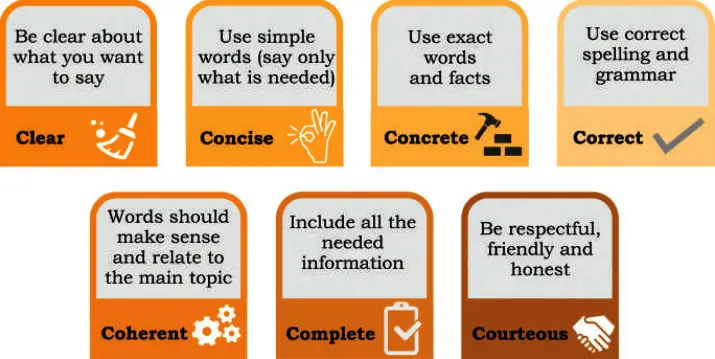
7Cs of Effective Communication![7Cs of Effective Communication]()
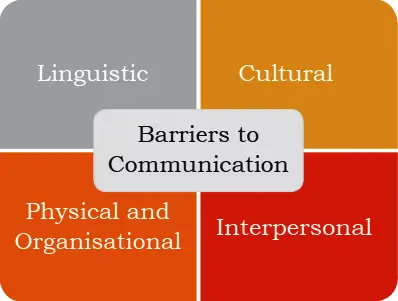
Barriers to Effective Communication![Barriers to Communication]()
Some common barriers to effective communication include:
- Physical Barriers: Physical barrier is the environmental and natural condition that act as a barrier in communication in sending message from sender to receiver. Not being able to see gestures, posture and general body language can make communication less effective. For example, text messages are often less effective than face-to-face communication.
- Linguistic Barriers: The inability to communicate using a language is known as language barrier to communication. Language barriers are the most common communication barriers, which cause misunderstandings and misinterpretations between people. For example, slang, professional jargon and regional colloquialisms can make communication difficult.
- Interpersonal Barriers: Barriers to interpersonal communication occur when the sender’s message is received differently from how it was intended. It is also very difficult to communicate with someone who is not willing to talk or express their feelings and views. Stage fear, lack of will to communicate, personal differences can create interpersonal barriers to communication.
- Organisational Barriers: Organisations are designed on the basis of formal hierarchical structures that follow performance standards, rules and regulations, procedures, policies, behavioural norms, etc. All these affect the free flow of communication in organisations and therefore, need to be suitably managed. For example, Superior-subordinate relationships in a formal organisational structure can be a barrier to free flow of communication.
- Cultural Barriers: Cultural barriers is when people of different cultures are unable to understand each other’s customs, resulting in inconveniences and difficulties. People sometimes make stereotypical assumptions about others based on their cultural background, this leads to difference in opinions and can be a major barrier to effective communication.
Ways to Overcome Barriers to Effective Communication
- Use simple language
- Do not form assumptions on culture, religion or geography
- Try to communicate in person as much as possible
- Use visuals
- Take help of a translator to overcome differences in language
- Be respectful of other’s opinions