Competency Based Questions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Chapter 5: The Fundamental Unit of Life provides competency based questions to deepen your understanding of cell biology. Engage with practical exercises, detailed solutions, and insightful explanations designed to enhance your grasp of cellular structures, functions, and processes. Ideal for students and educators aiming to master competency based assessments in biology.
Hint: Enumerate different types of cells commonly found in nature in order to establish that building units can differ with different organism.
Question.1. The image shows some types of cells.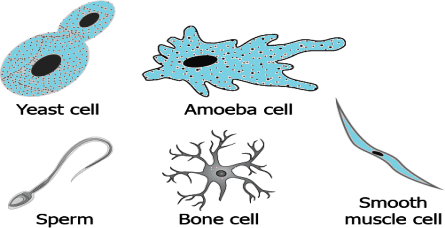
(a) to suit their function
(b) as they are formed first or last in the body
(c) as they are all animal cells
(d) as some are plant cells and some animal cells
Question.2. The image shows cells in the onion peel and human cheek.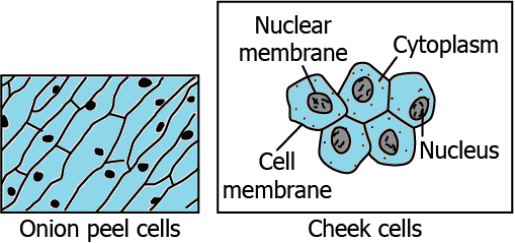
(a) All living things made of cells that look similar.
(b) All living things made up of cells that are structurally similar but functionally different.
(c) All living things are made up of cells that are functionally similar but structurally different.
(d) All living things are made of cells that look different from each other.
Ans.1. (a) to suit their function
Ans.2. (d) All living things are made of cells that look different from each other.
Hint: Demonstrate the difference between animal and plant cells with appropriate experiments.
Question.3. What will likely happen if an animal cell and a plant cell are placed in a sugar solution that has water concentration more than that of the animal cell and the plant cell?
(a) Both the animal and plant cell will burst.
(b) Both the animal and plant cell will swell.
(c) Animal cell will swell while the plant cell will burst.
(d) Animal cell will burst while the plant cell will swell.
Question.4. The image shows how the two cells appear before and after placing in a hypertonic solution.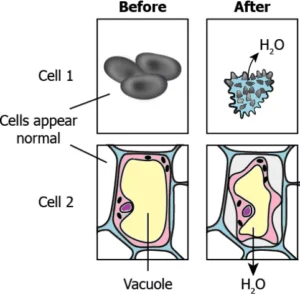
(a) Cell 1: animal cell, Cell 2: plant cell
(b) Cell 1: bacterial cell, Cell 2: plant cell
(c) Cell 1: Plant cell, Cell 2: animal cell
(d) Cell 1: animal cell, Cell 2: bacterial cell
Ans.3. (d) Animal cell will burst while the plant cell will swell.
Ans.4. (a) Cell 1: animal cell, Cell 2: plant cell
Hint: Compare a Prokaryotic and a Eukaryotic cell.
Question.5. What is a basis for differentiation of a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell?
(a) presence or absence of cytoplasm
(b) presence or absence of cell membrane
(c) presence or absence of genetic material
(d) presence or absence of membrane bound organelles
Question.6. The image shows a bacterial cell and an animal cell.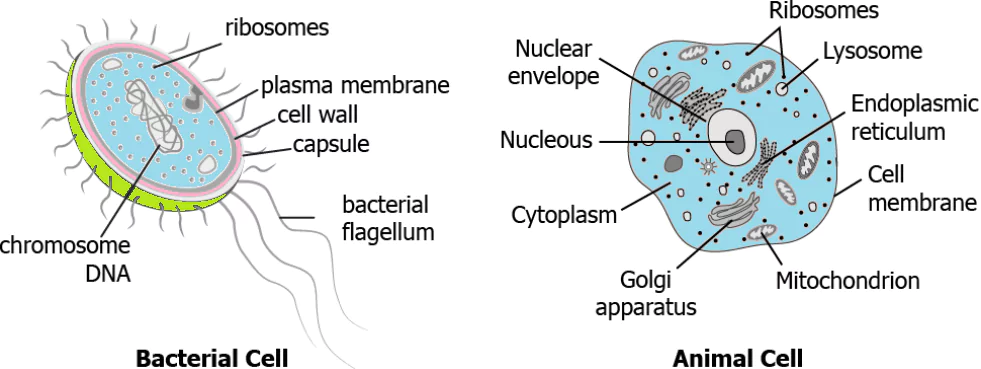
(a) Animal cell contains flagella that aids in locomotion that is absent in case of a bacterial cell.
(b) Nuclear material of the bacterial cell is not enclosed in a nuclear envelope as in case of an animal cell.
(c) Cytoplasmic content of the bacterial cell is not enclosed in a thick cell wall as in case of an animal cell.
(d) Animal cell contains ribosomes spread across the cell whereas in case of bacterial cell they are clumped together.
Ans.5. (d) presence or absence of membrane bound organelles
Ans.6. (b) Nuclear material of the bacterial cell is not enclosed in a nuclear envelope as in case of an animal cell.
Hint: Locate different cell organelles in a plant cell and state their functions.
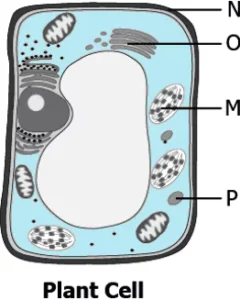
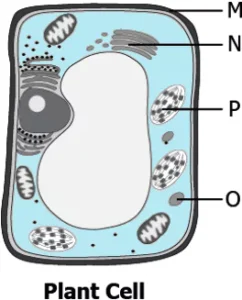
Question.7. The image shows a plant cell.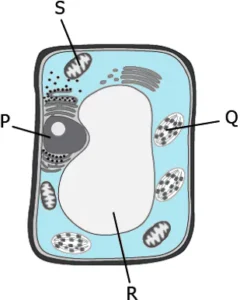
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
Question.8. The table lists functions performed by some plant cell organelles.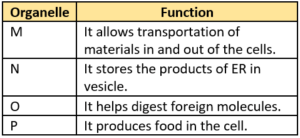
(a) 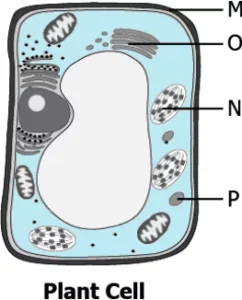

Question.9. Which of following is the function of cytoplasm present in the cell?
(a) It plays a central role in cellular reproduction.
(b) It is involved in the formation of lysosomes.
(c) It helps transport material into the cell.
(d) It holds the organelles of the cell in place.
Question.10. The table lists some functions performed by some cell structures.
(a) Cytoplasm- Q and S, nucleus- P, plasma membrane- R
(b) Cytoplasm- Q and R, nucleus- P, plasma membrane- S
(c) Cytoplasm- Q, nucleus- R, plasma membrane- S and P
(d) Cytoplasm- R, nucleus- Q, plasma membrane- S and P
Ans.7. (d) S
Ans.8. (b) 
Ans.10. (c) Cytoplasm- Q, nucleus- R, plasma membrane- S and P
Hint: Differentiate between types of endoplasmic reticulum and identify their functions.
Question.11. Which of the following function is performed by smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
(a) It helps expel excess water and waste out of the cell.
(b) It helps produced ATP molecules.
(c) It helps digest small foreign particles.
(d) It helps detoxify the drugs.
Question.12. How endoplasmic reticulum helps transport protein between various regions of the cytoplasm?
(a) by forming a network of membrane-bound tubes in the cytoplasm
(b) by occupying most of the space in the cytoplasm
(c) by generating small transport vesicles throughout the cell
(d) by directing all cell organelles to perform the same biochemical activity
Ans.11. (d) It helps detoxify the drugs.
Ans.12. (a) by forming a network of membrane-bound tubes in the cytoplasm
Hint: Name the cell organelle responsible for storage, modification and packaging of products in a cell.
Question.13. Proteins are synthesized near the endoplasmic reticulum. Where are these proteins transported further in the cell?
(a) to the nucleus
(b) to Golgi body
(c) to mitochondria
(d) to the cell membrane
Question.14. The function of Golgi body includes:
(a) degradation and elimination of waste substances
(b) storage, modification, and packaging of products in vesicles
(c) synthesis of lipids and proteins
(d) providing rigidity and turbidity to the cell
Ans.13. (b) to Golgi body
Ans.14. (b) storage, modification, and packaging of products in vesicles
Hint: Explain the functioning of Mitochondria in a cell.
Question.15. What is the main function of mitochondria?
(a) to stop the chemical reaction in the cell and store ATP as energy
(b) to perform all the chemical reactions of the cell using ATP
(c) to use energy currency in the form of ATP
(d) to produce ATP molecules
Question.16. A large amount of energy is required by the cell to carry out various cellular processes.
Which part of mitochondria helps generate enough energy required for various chemical activities and how?
(a) The folds present in the inner mitochondrial membrane decrease the surface area for more ATP production.
(b) The folds present in the inner mitochondrial membrane increase the surface area for more ATP production.
(c) The folds present in the outer mitochondrial membrane increase the surface area for more ATP production.
(d) The folds present in the outer mitochondrial membrane decrease the surface area for more ATP production.
Ans.15. (d) to produce ATP molecules
Ans.16. (b) The folds present in the inner mitochondrial membrane increase the surface area for more ATP production.
Hint: Relate the functions of Lysosomes in a cell.
Question.17. Which of the following are usually digested or degraded by lysosomes?
(a) ATP molecules
(b) oxygen molecules
(c) old organelles of the cell
(d) carbon dioxide molecules
Question.18. Anil has bacterial infection. Which part of the cell will help him eliminate bacteria from his body and how?
(a) Vacuoles as they can uptake any material and store it.
(b) Vacuoles as they can expel substance out of the cell.
(c) Lysosomes as they have digestive enzymes to breakdown foreign material.
(d) Lysosomes as they can destroy their own cell.
Ans.17. (c) old organelles of the cell
Ans.18. (c) Lysosomes as they have digestive enzymes to breakdown foreign material.
Hint: Locate the cell organelle that helps cells prepare their food.
Question.19. What is the function of chromoplast in a cell?
(a) It helps plant utilize energy.
(b) It helps plant breakdown food.
(c) It helps plant make food.
(d) It helps plant release energy to the surroundings.
Question.20. In plants, cells in the leaves mainly make food for the plant. Which organelle does these cells have that enables them to make food?
(a) These cells have plastids with pigment chlorophyll that helps photosynthesize.
(b) These cells have mitochondria that provides ATP as energy to photosynthesize.
(c) These cells have colorless plastids that absorb sunlight to help plant
photosynthesize.
(d) These cells have vacuoles that provide essential nutrients required for
photosynthesis.
Ans.19. (c) It helps plant make food.
Ans.20. (a) These cells have plastids with pigment chlorophyll that helps photosynthesize.
Hint: Elaborate the role of chromosomes during cell division.
Question.21. What is the role of centrosomes in cell division?
(a) It helps the cell to enlarge to undergo division
(b) It helps the cell to divide into two daughter cells.
(c) It helps join the chromosomes together.
(d) It helps separate sister chromatids apart.
Question.22. The image shows a stage of cell division.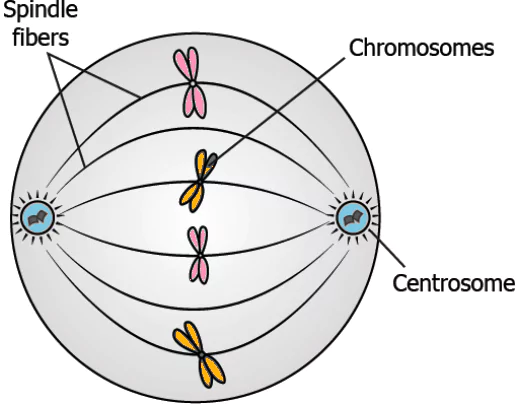
(a) It organizes spindle fibers and allows equal distribution of chromosome in the daughter cells.
(b) It forms spindle fibers before the cell division starts.
(c) It degrades the spindle fibers and chromosomes when the division completes.
(d) It releases spindle fibers that hold the chromosomes during division.
Ans.21. (d) It helps separate sister chromatids apart.
Ans.22. (a) It organizes spindle fibers and allows equal distribution of chromosome in the daughter cells.
Hint: Relate the role of vacuoles in a cell.
Question.23. What is the function of vacuoles?
(a) It digests sugars.
(b) It stores amino acids.
(c) It synthesis proteins.
(d) It encloses nuclear material.
Question.24. In summers, leaves of a potted plant droops when the soil becomes dry. Which cell organelle makes the leaves to droop?
(a) Nucleus, as it stops making DNA.
(b) Cell wall, as it starts to shrink.
(c) Lysosome, as it is releasing the digestive enzymes.
(d) Vacuole, as it loses all the water.
Ans.23. (b) It stores amino acids.
Ans.24. (d) Vacuole, as it loses all the water.