NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources
NCERT Solutions for Social Science Class 10 Contemporary India – II Chapter 2 Forest and Wildlife Resources contain the solutions to the In-chapter questions and exercises given in the Geography book – Contemporary India – II. In this chapter, students will mainly find questions related to the Forest and wildlife resources. These NCERT Solutions provide the answers to all questions in a simple and easy-to-understand way. Attempting these answers in the exam will surely help the students in scoring high marks.
NCERT Solutions
Intext Questions
Question.1. Find out stories prevalent in your region which are about the harmonious relationship between human beings and nature.
As area wise stories are different such as Chiplo Movement. So the answer is written in context of harmonious relationship between human beings and nature.
Ans. A truly harmonious relationship between humans and nature signifies a state of balance. We rely on nature for clean air, water, food, and resources, while also having a responsibility to protect its delicate ecosystems.
This harmony can be achieved through several practices:
- Sustainable practices: Minimizing waste, using renewable resources, and employing eco-friendly technologies all contribute to a healthier planet.
- Respectful interaction: Recognizing the intrinsic value of nature, not just its utility, fosters a deeper connection and encourages responsible actions.
- Conservation efforts: Protecting endangered species and preserving habitats ensures a thriving natural world for generations to come.
Living in harmony with nature isn’t about domination; it’s about recognizing our place within a complex and interconnected system. By respecting nature’s delicate balance, we ensure a healthier planet for ourselves and future generations.
Question.2. Have you noticed any activity which leads to the loss of biodiversity around you? Write a note on it and suggest some measures to prevent it.
Ans. Activities which lead to the loss of biodiversity are:
- The transformation of the natural areas results into the loss of the vegetable species and decrease in the animal species associated to them.
- Species originating from a particular area, introduced into new natural environments can lead to different forms of imbalance in the ecological equilibrium.
- Human activity influences the natural environment producing negative, direct or indirect, effects that alter the flow of energy, the chemical and physical constitution of the environment and abundance of the species.
- Heating of the Earth’s surface affects biodiversity because it endangers all the species that are adapted to the cold due to the latitude (the Polar species) or the altitude (mountain species).
- When the activities connected with capturing and harvesting (hunting, fishing, farming) a renewable natural resource in a particular area is excessively intense, the resource itself may become exhausted.
Precautions:
- Maintain wetlands by conserving water and reducing irrigation. Avoid draining water bodies on your property.
- Leave native plants undisturbed, and landscape using native trees and vegetation. Native plants are well adapted to local conditions and provide a low maintenance, drought resistant garden and can prevent local flooding.
- Use pesticides that have minimal residual effects.
- Don’t deteriorate the environment.
- Try to avoid wastage of energy.
- Recycle, reuse and reduce. Recycling decreases pollution by decreasing energy, electricity, and water consumption and the need for landfills.
- Use natural products and avoid buying things which are made from animal skins, shells, feathers, etc.
- Encourage and support local government initiatives that protect habitat and decrease threats to biodiversity.
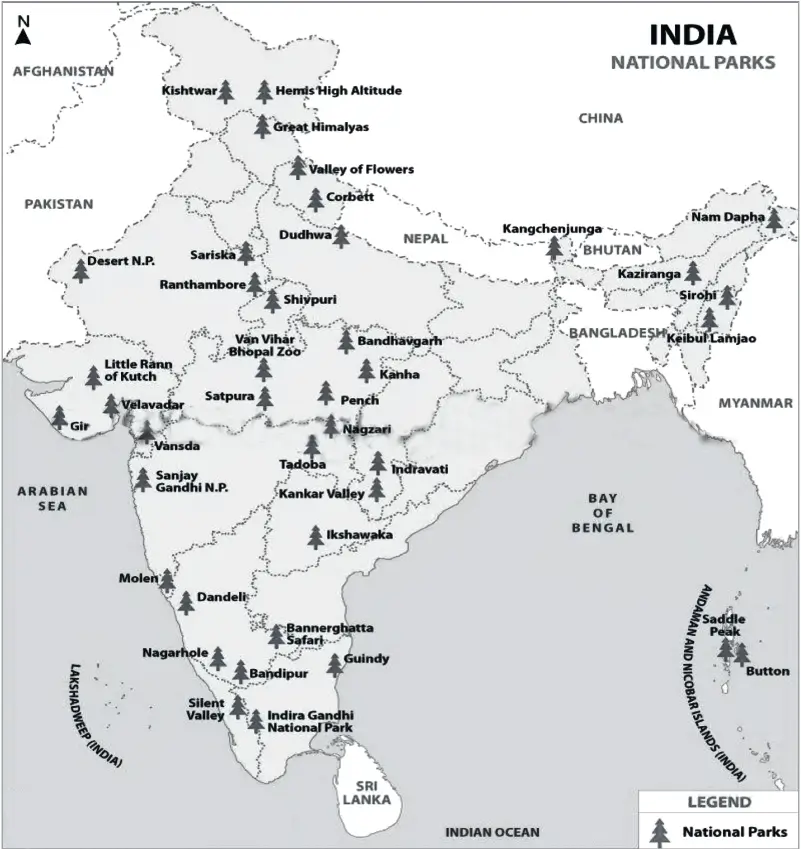
Question.3. Collect more information on the wildlife sanctuaries and national parks of India and cite their locations on the map of India.
Ans. National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries are protected areas declared by Government with the primary objective to preserve wildlife, save flora & fauna and restore the natural ecological balance. There are 104 National Parks (as in January 2021) and 544 Wildlife Sanctuaries in India. Madhya Pradesh and Andaman have the maximum number of National Parks (11). The spectacular natural beauty across the national parks and wildlife sanctuaries in India attracts millions of tourists every year.
Question.4. Write a short essay on any practices which you may have observed and practised in your everyday lives that conserve and protect the environment around you.
Ans. There are no such customs around us. Some people are interested in the environment, they plant trees and some people plant saplings in the memory of their ancestors or those who have love for trees and plants and like greenery, they plant trees, that is, There is no special custom for this. Example – Chipko movement.
Ways to conserve and protect the environment around us:
- Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle: Cut down on what you throw away.
- Follow the three R’s to conserve natural resources and landfill space.
- Conserve water: The less water you use, the less runoff and wastewater that eventually end up in the ocean.
- Shop wisely: Buy less plastic and bring a reusable shopping bag.
- Use long-lasting light bulbs: Energy efficient light bulbs reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Conserve electricity: Turn the light switch off when you leave the room!
- Plant a tree: Trees provide food and oxygen. They help save energy, clean the air, and help combat climate change.
- Bike more: Drive less.
- Volunteer: Volunteer for cleanups in your community. You can get involved in protecting your watershed, too.
- Educate: When you further your own education, you can help others understand the importance and value of our natural resources.
- Don’t send chemicals into our waterways: Choose non-toxic chemicals in the home and office.
Question.5. 
Ans. India’s special crocodilian Gharial population is the biggest concern for the wildlife lovers, Due to the river pollution, loss of riverine habitat and fishing gill nets, the Gharial came to the brink of extinction and fall in the critically endangered category.
The same goes for the birds as these birds which fed on the fishes of Yamuna river were contaminated by the harmful pollutants released into the rivers.
Important Facts & Questions on National Parks in India
Question.1. What is a National Park?
Ans. Any natural habitat which is set aside by the Government of a state or Union Territory for the conservation of the natural environment is called a National Park.
Question.2. Which is the first national park established in India?
Ans. India’s first national park was established in 1936 as Hailey National Park, now known as Jim Corbett National Park, Uttarakhand.
Question.3. Which is the largest National Park in India?
Ans. Hemis National Park in Ladakh is the largest National Park in India. Hemis National Park is globally famous for its snow leopards, it is believed to have the highest density of them in any protected area in the world.
Question.4. What is the largest and smallest Biosphere reserve in India?
Ans. The largest Biosphere reserve in India is the Gulf of Kachchh, Gujarat, and the smallest Biosphere Reserve in India is Dibru-Saikhowa in Assam.
Question.5. Why do we need National Parks?
Ans. There are multiple objectives for creating a National Park:
- It can help in the protection of the ecosystem os a specific area or region
- Conservation of species that are on the verge of extinction
- To preserve natural resources for ecological development
- It can help in preserving varied species
Question.6. Which was the first Marine National Park in India?
Ans. The first Marine National Park is located in the Gulf of Kutch and was created in 1982. It is situated on the southern shore of the Gulf of Kutch in the Devbhumi Dwarka district of Gujarat state.
Question.7. Which is the only floating National Park in the country and where is it located?
Ans. The Keibul Lamjao National Park is a national park in the Bishnupur district of the state of Manipur in India. It is the only floating National Park in the world.
Question.8. What is the difference between a National Park and a Wildlife Sanctuary?
Ans. A wildlife sanctuary is an area of nature owned by the government or a private agency for the protection of particular species of flora or fauna during a part of the year or in its entirety. Whereas, a national park is a reserved area of land owned by the government which is protected from industrialization, human exploitation, and pollution.
Question.9. Which is the oldest National Park in India?
Ans. The Jim Corbett National Park is the oldest National Park in India. It is located in Uttrakhand and was established in 1936.
Question.10. How many National Parks are there in India?
Ans. There are a total of 104 National Parks (as in January 2021) in India. They cover a total area of 40,564 sq. km, which is 1.23% of the geographical area of the country.
Question.11. What is the difference Between Wildlife Sanctuary, Biosphere Reserves and National Park?
Ans.
- Wildlife Sanctuary: A wildlife sanctuary is an area of nature owned by the government or a private agency for the protection of particular species of flora or fauna during a part of the year or in its entirety.
- National Park: A national park is a reserved area of land owned by the government which is protected from industrialization, human exploitation, and pollution.
- Biosphere Reserve: A biosphere reserve is a term given to an area for the conservation of the resources of the biosphere and the improvement of the relationship between man and the environment.
Question.12. What are the objectives of National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries?
Ans. Objectives of National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries:
- Provide safe habitat to protect wildlife from poaching and other human activities.
- Promote conservation of flora and fauna
- Preserve the geological and ecological balance of the area.
- Provide required resources for the livelihoods of local people.
- Preserve our culture and tradition through wildlife.
- Protect biodiversity for sustainable development.
- Produce revenue by tourism, ecotourism etc.
- Help in preservation of endangered animal species through working with local communities as a partner to develop their economic potential, increase their human resources and also improve their living standards.
Question.13. How many national parks are in Madhya Pradesh?
Ans. There are 11 National parks in Madhya Pradesh covering an area of 4349.14 Sq. Km. The name of eleven National parks in Madhya Pradesh are:
- Bandhavgarh National Park
- Dinosaur Fossil National Park
- Mandla Fossil National Park
- Kuno National Park
- Indira Priyadarshini Pench National Park
- Kanha National Park
- Madhav National Park
- Panna National Park
- Sanjay National Park
- Satpura National Park
- Van Vihar National Park
TEXTBOOK EXERCISE
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Question.1. Which of the following conservation strategies do not directly involve community participation?
(A) Joint forest management
(B) Beej Bachao Andolan
(C) Chipko Movement
(D) Demarcation of Wildlife sanctuaries
Ans. (D) Demarcation of Wildlife sanctuaries
II. Match the following.
| Reserved forests | other forests and wastelands belonging to both government and private individuals and communities |
| Protected forests | forests are regarded as most valuable as far as the conservation of forest and wildlife resources |
| Unclassed forests | forest lands are protected from any further depletion |
Ans.
| Reserved forests | forests are regarded as most valuable as far as the conservation of forest and wildlife resources |
| Protected forests | forest lands are protected from any further depletion |
| Unclassed forests | other forests and wastelands belonging to both government and private individuals and communities |
III.Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
Question.1. What is biodiversity? Why is biodiversity important for human lives?
Ans. Biodiversity refers to diverse flora and fauna that exist in a given area.
Biodiversity is made up of various types of life forms found on earth.
Contribution of biodiversity in human lives. Plants, animals and human beings are interdependent. It is necessary for human beings as we get fresh air, water, food, etc., from them. Thus, the existence of human beings depends on them.
Question.2. How have human activities affected the depletion of flora and fauna? Explain.
Ans. Human activities and man’s insensitivity to the environment have been the major causes for the depletion of flora and fauna. Following are the few activities leading to such causes-
- Deforestation for agricultural expansion
- Degradation of forests by shifting cultivation
- Large scale development projects
- Mining activities
- Habitat destruction, hunting, poaching, over exploitation of forest products, environmental degradation, forest fires.
IV. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
Question.1. Describe how communities have conserved and protected forests and wildlife in India?
Ans.
- Chipko Movement : The famous Chipko movement in the Himalayas has not only successfully resisted deforestation in several areas but has also shown that community afforestation with indigenous species can be enormously successful.
- Certain societies revere a particular tree which they have preserved from time immemorial. The Mundas and the Santhal of Chota Nagpur region worship mahua (Bassia latifolia) and kadamba (Anthocephalus cadamba) trees, and the tribals of Odisha and Bihar worship the tamarind (Tamarindus indica) and mango (Mangifera indica) trees during weddings. To many of us, peepal and banyan trees are considered sacred.
- In Sariska Tiger Reserve, Rajasthan, villagers have fought against mining by citing the Wildlife Protection Act. In many areas, villagers themselves are protecting habitats and explicitly rejecting government involvement. The inhabitants of five villages in the Alwar district of Rajasthan have declared 1,200 hectares of forest as the Bhairodev Dakav ‘Sonchuri’, declaring their own set of rules and regulations which do not allow hunting and are protecting the wildlife against any outside encroachments.
Question.2. Write a note on good practices towards conserving forest and wildlife.
Ans. For the conservation of forests many good practices have been evolved. These include:
- Worshiping of trees and animals.
- Use of flora and fauna in religious functions.
- Formation of national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and bio reserves to protect endangered species.
- Punishable penal codes on killing animals.
- Community programs like Vanmahotsav etc. to bring awareness among the people about the importance of wildlife.
- Regulated and Planned Cutting of Trees.
- Control over Forest Fire.
- Reforestation and Afforestation.
- Check over Forest Clearance for Agricultural and Habitation Purposes.
- Proper Utilization of Forest and Forests Products.