Revision Notes for Class 10 IT (402) – Chapter 2 Self Management Skills II
Self Management Skills
- Self Management Skills are those skills that help a person to control his thoughts, wants, feelings and actions. It allows you to maximize your productivity and performance in various fields of your career.
- When we talk about employability, Self-management skills help you to manage a good career path. It helps you to overcome in many bad situations. Here in this article, we will discuss Stress and Stress Management Techniques and also we will discuss how to work independently.
Following are some of the skills you must master to succeed in life:
- Self-awareness: Ask for honest feedback. Gather insights on your personality and work-specific proficiencies. Think about your daily interactions and how you handled situations well or could have handled them differently.
- Responsibility: Taking responsibility for your tasks is very important. Taking ownership is the step towards self-development. For example, if you have been assigned a task by a teacher; ensure you take complete ownership. Even if you are unable to complete the task on time, you must report it and then correct it.
- Time Management: Prioritise the things you have to do. Remove waste and redundancy from work. Make a time table and follow it diligently.
- Adaptability: Stay current with best practices and read up on new information always. Prepare yourself for new changes, so that you can transition seamlessly.
What is Stress?
Stress can be defined as our emotional, mental, physical and social reaction to any perceived demands or threats. These demands or threats are called stressors. Stressors are the reason for stress.
For example,
- you are too close to the exams but feel unprepared.
- you are experiencing a loss of someone close in the family.
- you are worried about what people would think of you if you don’t dress well or cannot speak confidently.
Stress Management
Managing stress is about making a plan to be able to cope effectively with daily pressures. The ultimate goal is to strike a balance between life, work, relationships, relaxation, and fun. By doing this, you are able to deal with daily stress triggers and meet these challenges head-on.
Always keep in mind the ABC of stress management
A: Adversity or the stressful event
B: Beliefs or the way you respond to the event
C: Consequences or actions and outcomes of the event
Ability to Work Independently
If you can become a calm and relaxed person, you will have the ability to work independently, which means.
- becoming self-aware, self-monitoring, and self-correcting.
- knowing what you need to do.
- taking the initiative rather than being told what to do.
- recognising your mistakes and not blaming others.
- having the ability and the will to learn continuously.
Three Steps to Manage Stress
Management Techniques
Here are a few simple stress management techniques.
- Time management: Proper time management is one of the most effective stress-relieving techniques.
- Physical exercise and fresh air: A healthy lifestyle is essential for students. Stress is generally lower in people who maintain a healthy routine. Doing yoga, meditation and deep breathing exercises help in proper blood circulation and relaxes the body. Even taking a walk or playing in the park will help you get a lot of fresh oxygen, which will help you become more active.
- Healthy diet: Having a healthy diet will also help you reduce stress. Eating a balanced diet, such as Dal, Roti, vegetables and fruits will give you the strength to do your daily work efficiently.
- Positivity: Focussing on negative aspects of life will add more stress. Instead, learn to look at the good things and stay positive. For example, instead of feeling upset over a scoring less in a test, try to maintain a positive attitude and look at ways to improve the next time.
- Sleep: We should get a good night’s sleep for at least 7 hours so that your brain and body gets recharged to function better the next day.
- Holidays with family and friends: Going to a relative’s place, such as your grandparents’ house or a new place during your summer vacations can help you break from the normal routine and come back afresh.
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to identify and manage one’s own emotions, as well as the emotions of others.
- Emotional awareness : the ability to identify and name one’s own emotions.
- Harnessing emotions : the ability to harness and apply emotions to tasks like thinking and problem solving.
- Managing emotions : the ability to regulate one’s own emotions when necessary and help others to do the same.
Some steps to manage emotional intelligence are as given below.
- Understand your emotions: Observe your behaviour and note the things you need to work on. You can then work on the things you need to improve.
- Rationalise: Do not take decisions abruptly; be rational in your thinking.
- Practice: Do meditation and yoga to keep yourself calm.
Techniques for Identifying your Strengths and Weaknesses
Finding Strengths (or abilities)
- Think of anything that you are always successful at.
- Think about what others like in you.
- Take out time and think about what you do well.
Finding Weaknesses
- Point out the areas where you struggle and the things you find difficult to do.
- Look at the feedback others usually give you.
- Be open to feedback and accept your weaknesses without feeling low about it. Take it as an area of improvement.
Difference between Interests and Abilities (Strengths)
Interests
- Things that you like to do in your free time that make you happy. An acquired or natural capacity
- Things you are curious about or would do even if no one asked you to do it.
- Things you want to learn or would like to do in the future
Ability
- An acquired or natural capacity
- Enable you to perform a particular job or task with considerable proficiency.
Self-motivation
Self-motivation is simply the force within you that drives you to do things. Self-motivation is what pushes us to achieve our goals, feel happy and improve our quality of life. In other words, it is our ability to do the things that need to be done without someone or something influencing us.
Types of Motivation
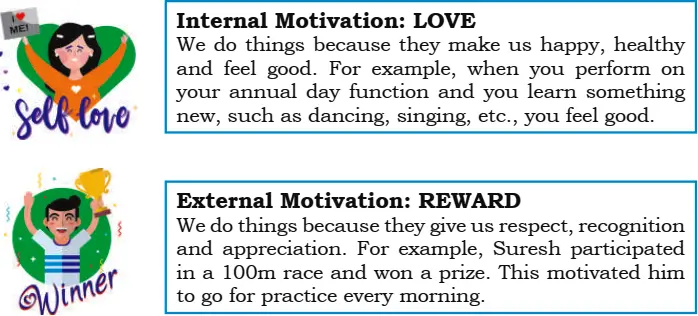
- Internal Motivation – We do things because they make us happy, healthy and feel good. For example, when you perform on your annual day function and you learn something new, such as dancing, singing, etc., you feel good.
- External Motivation – We do things because they give us respect, recognition and appreciation. For example, Suresh participated in a 100 m race and won a prize. This motivated him to go for practice every morning.
Qualities of Self-motivated People
- Know what they want from life
- Are focussed
- Know what is important
- Are dedicated to fulfill their dreams
Building Self-motivation
- Find out your strengths
- Set and focus on your goals
- Develop a plan
- to achieve your goals
- Stay loyal to your goals
Types of Motivation![Types of Motivation]()
Goals: They are a set of dreams with a deadline to get them, for example, saving pocket money to buy a favourite mobile phone by a particular date.
Goal setting: It is all about finding and listing your goals and then planning on how to achieve them.
How to Set Goals?
We can use SMART method to set goals. SMART stands for: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Time Bound
- Specific : A specific and clear goal answers six questions. Who is involved in the goal? What do I want to do? Where do I start? When do I start and finish? Which means do I use? Why am I doing this? Not a specific goal: “I would learn to speak English.” Specific goal: “I would learn to speak English fluently by joining coaching classes after my school everyday, and in six months I will take part in the inter-school debate competition.”
- Measureable : A measureable goal answers the questions “How much?”, “How many?” and “How do I know that I have achieved results?” Not measurable goal: “I want to be rich.” Measurable goal: “I want to have 5 times more money than what I have today in my hand at the end of this year.”
- Achievable : Breaking down big goals into smaller parts will make the goal achievable. Bigger Goal: “I want to become a teacher in my school.”
- Realistic : A realistic goal would be something that we want to achieve and can work towards. Example of unrealistic goal: “I will read my entire year’s syllabus in one day and get good marks.” Realistic goal: “I spend 3 hours every day of the year after school to revise my subjects to get good marks in the exams.”
- Time bound : A SMART goal should have a timeframe by when the goal needs to be achieved. This encourages us to take actions to completely fulfill the goals. Not a time bound goal: “I want to lose 10 kg someday.” Time bound goal: “I want to lose 10 kg in the next 6 months.”
Time Management and Its Importance
Time management is the thinking skill that helps you to
- complete tasks on time.
- make a daily timetable.
- make a good guess at how long it will take you to do something.
- submit homework and assignments on time.
- not waste time during the day.
Four Steps for Effective Time Management Organise
- Organise: We plan our day to- day activities.
- Pritortis: We make a to-do list that has all our activities and we rank them in the order of importance.
- Control: We have a control over our activities and time.
- Track: We identify and note where we have spent our time.